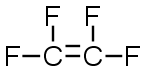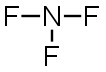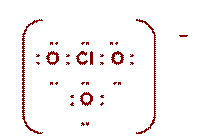Unit II
Atomic Theory
Worksheets
Lesson Date Topic WS
#
5. Mass Spectrometer/ Elegant Universe-1 5
6. Elegant Universe-2/Periodic Chem 6
8. Classifying Matter Lab 8
9. Classifying and Naming Formulas 1 9
10. Classifying and Naming Formulas 2 10
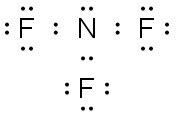
11. Electron Dot Diagram Structural Formula 1 11
13. Practice Test 1 13
14. Practice Test 2 14
15.
Test
Worksheet # 1 Early
Atomic Theory
Briefly
describe each atomic theory listed below.
Include a diagram.
1. The Four-Element Theory
The Four Element
Theory
(a) evidence (b)
explanation within theory
No
evidence Nonscientific
Theory
2.
(a) Evidence (b)
Explanation within theory
Conservation of
mass Atoms
are indestructible
Law of Constant
composition Elements
combine in simple ratios
3. The Thompson Atom
(a) Evidence (b)
Explanation within theory
Electrical Nature
of Matter Positive
and negative particles
Worksheet # 2 Early Atomic Theory
1. The Rutherford Atom
(a) Evidence (b)
Explanation within theory
A few alphas are
radically deflected Small dense
nucleus
Most alphas are
not deflected Most of
atom is empty space
2. The Bohr Atom
The Bohr Atom
(a) evidence (b)
explanation within theory
Line
spectrum of discharge tubes Electrons
are in orbitals
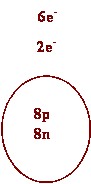
Draw
Bohr atomic diagrams for the following atoms.
Be sure to include protons, neutrons and electrons.
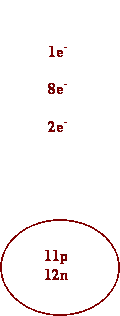
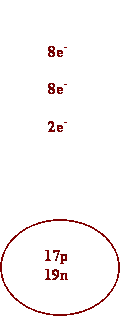
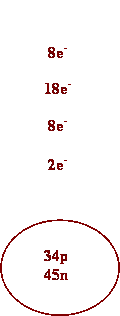
1. Oxygen 7.
Calcium
2. Silver 8. Barium
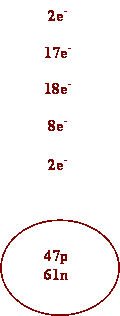
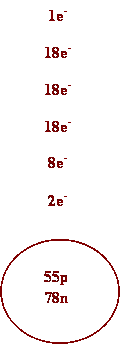 3. Cs 9. I
3. Cs 9. I
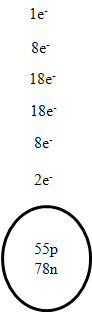
4. Na 10. V
5. Cl- 11. Al3+
6.
Se2- 12. Ca2+
Worksheet #4 Quantum
Mechanics
1. What is the main difference between the
Bohr Theory of the atom and the Quantum Mechanical Theory?
Electrons
are waves in Quantum Theory and particles in the Bohr Theory.
2. How many electrons will fill the smallest
orbital in quantum mechanical theory?
Two
3. How is a 3s orbital different than a 2s
orbital in terms of shape and distance from the nucleus?
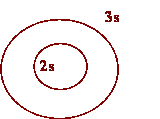
They are
both spherical in shape but the 3s is further from the nucleus.
4. Explain what happens to the energy when an
electron falls from a 3s orbital to a 2s orbital.
Energy
is emitted in the form of a photon of light with energy corresponding to the
difference between the two orbitals.
Use
your Quantum Periodic Table to write quantum electron configurations for each
element below.
5. F 1s22s22p5
6. K 1s22s22p63s23p64s1
7. C 1s22s22p2
8. Kr 1s22s22p63s2 3p63d104s24p6
9. S 1s22s22p63s23p4
10. Rb 1s22s22p63s2
3p63d104s24p65s1
11. Co 1s22s22p63s2 3p63d74s2
12. P 1s22s22p63s2 3p3
13. Ca 1s22s22p63s2 3p64s2
14. Al 1s22s22p63s2 3p1
15. Ag 1s22s22p63s2 3p63d104s24p64d95s2
16. 1s22s22p63s1 Na
17. 1s22s22p63s23p5 Cl
18. 1s22s22p63s23p63d94s2 Cu
19. 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p5 I
20. 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d104f145s25p66s2
Ba
21.
Give the formula of four chemical species that are isoelectronic (same electron configuration) as Ar.
S2- P3- Cl- K+ Ca2+
Worksheet # 5 Mass
Spectrometry
Calculate
the average atomic mass for each element.
Round off to the correct number of sig figs. Write down the atomic mass from the periodic
table rounded off to the same number of sig figs.
Isotope Mass %
Abundance Average Mass Atomic Mass (table)
1.
14N 14.0030744 99.6340 14.0067 amu 14.0067 amu
15N 15.000108 0.366001
0.996340(14.0030744) + 0.00366001(15.000108) =
14.0067 amu
2.
20Ne 19.992404 90.92 20.2 amu 20.1798 amu
21Ne 20.993849 0.257
22Ne 21.991385 8.82
0.9092(19.992404) + 0.00257(20.993849) +
0.0882(21.991385) = 20.2 amu
3.
46Ti 45.952633 7.93 47.9 amu 47.90 amu
47Ti 46.95176 7.28
48Ti 47.947948 73.94
49Ti 48.947867 5.51
50Ti 49.944789 5.34
You will
lose marks if you don’t show the work!
4.
54Fe 53.93962 5.8202 55.847 amu 55.845 amu
56Fe 55.93493 91.660
57Fe 56.93539 2.1901
58Fe 57.93327 0.33001
You will lose
marks if you don’t show the work!
5. Silver has two common
isotopes. One is 106.90508 amu and 51.35 % and the
other is 48.65 %. If the average atomic
mass is 107.9730 amu, what is the atomic mass of the
other isotope?
106.90508
(.5135) + X (0.4865)
= 107.9730 amu
NOW SOLVE FOR X
109.1 amu
6.
Copper has two common isotopes. One is 62.92959 amu and 69.09 % and the other is 30.91 %. If the average atomic mass is 63.5472 amu, what is the atomic mass of the other isotope.
62.92959
(.6909) + X (0.3091)
= 63.5472 amu
NOW SOLVE FOR X
64.92 amu
7. Complete the chart below.
|
|
protons |
electrons |
neutrons |
|
28Si |
14 |
14 |
14 |
|
29Si |
14 |
14 |
15 |
|
30Si |
14 |
14 |
16 |
8. Write a quantum electron configuration for
each of the following.
a) Ne 1s22s22p6
b) Mg
c) Ti 1s22s22p63s2 3p63d24s2
d) Cr
e) Sr 1s22s22p63s2
3p63d104s24p65s2
f) Ag
g) Br 1s22s22p63s2 3p63d104s24p5
9. What was the first atomic theory to
account for the Law of Conservation of Mass?
Explain how the theory accomplished
this.
10.
What was the first atomic theory to
account for electromagnetic radiation (light)?
Explain how the theory accomplished
this.
Bohr
Theory. Electrons
are in orbitals.
11. What was the first atomic theory to account
for the small, dense nucleus?
Explain how the theory accomplished
this.
Rutherford
Atom. A few alpha particles were
radically deflected.
12.
What was the first atomic theory to
have a wave theory for the electron?
Explain how the theory accomplished
this.
Quantum Theory. Electrons
vibrate around the nucleus in 3 dimensional wavelike orbitals.
13.
What was the first atomic theory to
account for positive and negative charges in matter? Explain how the theory accomplished this.
Thomson Atom.
The matter in the atom was positive with negative particles throughout.
Worksheet # 6 Periodic
Chemistry
1. Define the following:
a) Oxidation Loss of electrons
b) Reduction Gain of electrons
c) Anion Negative ion
d) Cation Positive
ion
e)
Atom Neutral
particle of an element
f) Chemical family Column on Periodic Table
g) Period Row on Periodic Table
2. Why are noble gases stable? Full outer or
valence shells
3. Why are non-noble gases un-stable or
reactive? Incomplete
outer or valence shells
4. Draw Bohr diagrams for the following
chemical species.
 a) He b)
K
a) He b)
K
c) K+ d) S2-
e) P3- f) Li+

5. Fill in the chart below.
|
symbol |
atom, cation or anion |
protons |
neutrons |
electrons |
valence electrons |
stable or reactive? |
|
Mg2+ |
cation |
12 |
12 |
10 |
8 |
stable |
|
Mg |
atom |
12 |
12 |
12 |
2 |
unstable |
|
F |
atom |
9 |
10 |
9 |
7 |
unstable |
|
F- |
anion |
9 |
10 |
10 |
8 |
stable |
|
Ne |
atom |
10 |
10 |
10 |
8 |
stable |
|
C |
atom |
6 |
6 |
6 |
4 |
unstable |
|
Be |
atom |
4 |
5 |
4 |
2 |
unstable |
|
Be2+ |
cation |
4 |
5 |
2 |
2 |
stable |
|
N3- |
anion |
7 |
7 |
10 |
8 |
stable |
1.
|
symbol |
atom, cation or anion |
protons |
neutrons |
electrons |
valence electrons |
stable or reactive? |
|
Ga |
Atom |
31 |
39 |
31 |
3 |
Reactive |
|
Ga3+ |
Cation |
31 |
39 |
28 |
18 |
Stable |
|
Br |
Atom |
35 |
45 |
35 |
7 |
Unstable |
|
Br- |
Anion |
35 |
45 |
36 |
8 |
Stable |
|
Kr |
Atom |
36 |
48 |
36 |
8 |
Stable |
|
Ca |
Atom |
20 |
20 |
20 |
2 |
Unstable |
|
Ca2+ |
Cation |
20 |
20 |
18 |
8 |
Stable |
|
P |
Atom |
15 |
16 |
15 |
5 |
Unstable |
|
P3- |
Anion |
15 |
16 |
18 |
8 |
Stable |
2. What happens to protons, electrons and
neutrons as you move form left to right within a row
on the periodic table?
Protons,
Electrons, and Neutrons all increase.
3. Write half-reactions to show how each atom
forms an ion. Label each as oxidation or reduction. The first two are done for
you.
a) K → K+ + 1e- oxidation
b) N2 + 6e- → 2N3- reduction
c) P + 3e- → P3- reduction
d) O2 + 4e- → 2O2- reduction
e) Ca → Ca2+ +
2e- oxidation
f) Br2 + 2e- → 2Br- reduction
g) I2 + 2e- → 2I- reduction
h) Al → Al3+ +
3e- oxidation
i)
Ba → Ba2+ +
2e- oxidation
j) Cs → Cs+ + 1e- oxidation
k) Mg → Mg2+ +
2e- oxidation
l) Zn → Zn2+ +
2e- oxidation
m) Ga → Ga3+ +
3e- oxidation
n) Cl2 + 2e- → 2Cl- reduction
o) F2 + 2e- → 2F- reduction
4. Describe five properties of:
a) Metals
Shiny Conductors Malleable Ductile Lose electrons Left
side of periodic table
b) Non-metals
Dull Nonconductors Brittle Gain
electrons Right side of
periodic table
5. Draw Bohr diagrams for each of the
following.
a) Na b)
Na+
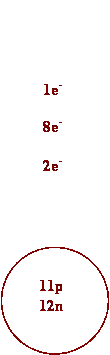
c) O d)
O2-

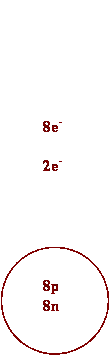
e) Ca f)
Ca2+
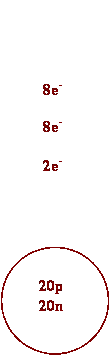
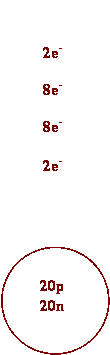
1. Complete the table.
|
|
Salt |
Base |
Acid |
Covalent Nonacid |
|
Litmus |
Neutral |
Blue |
Red |
Neutral |
|
Conductivity |
Good |
Good |
Good |
Non |
2. Put each formula into the table below.
Ca(OH)2 NH4OH CH3OH C12H24O11
HCl PI3 K2SO4 RbOH
H3PO4 NaOH CaCl2 Li2SO4
H2SO3 BaF2 BCl5 CH3COOH
H2CO3 CsOH S2Cl2 Fr2S
|
Salt |
Base |
Acid |
Covalent Nonacid |
|
K2SO4 |
Ca(OH)2 |
HCl |
CH3OH |
|
CaCl2 |
NH4OH |
H3PO4 |
C12H24O11 |
|
Li2SO4 |
RbOH |
H2SO3 |
PI3 |
|
BaF2 |
NaOH |
CH3COOH |
BCl5 |
|
Fr2S |
CsOH |
H2CO3 |
S2Cl2 |
3. Draw Bohr diagrams for each of the
following.
a) K+ b)
P3-
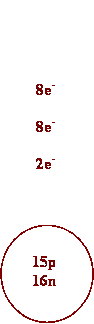

4. Write half-reactions to show how each atom
forms an ion. Label each as oxidation or reduction. The first two are done for you.
a) Ca → Ca2+ + 2e- oxidation
b) O2 + 4e- → 2O2- reduction
c) I2 + 2e- → 2I- reduction
d) N2 + 6e- → 2N3- reduction
e) Cs → Cs+ + e- oxidation
f) Ba → Ba2+ + 2e- oxidation
g) Al → Al3+ + 3e- oxidation
h) F2 + 2e- → 2F- reduction
i) H2 → 2H+ + 2e- oxidation
j) Na+ + 1e- → Na(s) reduction
k) N3- → N2 + 6e- oxidation
l) Ca2+ + 2e- → Ca reduction
m) Ba2+ + 2e- → Ba reduction
1. Complete the following table by
classifying and naming each compound.
|
Formula |
Classification |
Name |
|
CuS(s) |
Salt |
Copper II sulphide |
|
H3PO4(s)
|
covalent nonacid
(acids must be aq) |
Hydrogen
phosphate |
|
P2O5(s)
|
Nonacid |
Diphosphorus pentoxide |
|
NH4OH(s)
|
Base |
Ammonium
hydroxide |
|
Al2O3(s)
|
Salt |
Aluminum
oxide |
|
MgSO4(s)
|
Salt |
Magnesium
sulphate |
|
HCl(g)
|
covalent nonacid (acids must be aq) |
Hydrogen
chloride |
|
HCl(aq)
|
Acid |
Hydrochloric
acid |
|
H2SO4(l)
|
covalent
nonacid (acids must be aq) |
Hydrogen
sulphate |
|
H2SO4(aq)
|
Acid |
Sulphuric acid |
|
NI3(s)
|
Nonacid |
Nitrogen triiodide |
|
N3Cl3(s)
|
Nonacid |
Trinitrogen trichloride |
|
CO(g)
|
Nonacid |
Carbon
monoxide |
|
K2CrO4(s)
|
Salt |
Potassium
chromate |
|
H2Cr2O7(aq)
|
Acid |
Dichromic acid |
|
H2O(l)
|
Nonacid |
Water |
|
CrCO3(s)
|
Salt |
Chromium II
carbonate |
|
HBr(g)
|
covalent nonacid (acids must be aq) |
Hydrogen
bromide |
|
P3O5(s)
|
Nonacid |
Triphosphorus pentoxide |
2. Complete the following
table by classifying and naming each compound.
|
Formula |
Classification |
Name |
|
HI (aq)
|
Acid |
Hydroiodic acid |
|
(NH4)3PO4(s)
|
Salt |
Ammonium
phosphate |
|
NCl3(l)
|
Nonacid |
Nitrogen trichloride |
|
Ba(OH)2(s)
|
Base |
Barium
hydroxide |
|
Rb2SO4(s)
|
Salt |
Rubidium
sulphate |
|
CuCl2(s)
|
Salt |
Copper II
chloride |
|
Al2O3(aq)
|
Salt |
Aluminum
oxide |
|
N3Cl3(aq)
|
Nonacid |
Trinitrogen trichloride |
|
CO(g)
|
Nonacid |
carbon
monoxide |
|
H2SO3(aq)
|
Acid |
Sulphurous acid |
|
CuSO4 . 6H2O(aq)
|
Salt |
Copper II
sulphate hexahydrate |
|
H3PO3(s)
|
covalent nonacid (acids must be aq) |
Hydrogen phosphite |
|
Mg3(PO4)2(aq)
|
Salt |
Magnesium
Phosphate |
|
HCH3COO(aq)
|
Acid |
Acetic Acid
or Ethanoic acid |
|
HF(aq)
|
Acid |
Hydrofluoric
acid |
|
N2O5(aq)
|
Nonacid |
Dinitrogen pentoxide |
|
Na3PO4
. 5H2O(aq)
|
Salt |
Sodium
phosphate pentahydrate |
|
Ni(NO3)3(aq)
|
Salt |
Nickel III
nitrate |
|
SO(g)
|
Nonacid |
|
Use
your Quantum Periodic Table to write quantum electron configurations for each
element below.
3. Sr 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p65s2
4. V 1s22s22p63s23p63d34s2
5. Mg 1s22s22p63s2
6. P 1s22s22p63s23p3
7. Cr 1s22s22p63s23p63d44s2
Pick the best answers. Answers can be used more than once.
Answers: Four Element
Theory
Dalton’s
Atomic Theory
Thomson’s
Atomic Theory
Rutherford’s
Atomic Theory
Bohr’s
Atomic Theory
Quantum
Mechanical Theory
8.
9. Bohr’s
Atomic Theory The 1st model to explain light
10.
11.
12. Quantum
Mechanical Theory The 1st model to have an electron as a wave
13.
Four
Element Theory Non-scientific
Theory
14.
Thomson’s
Atomic Theory The 1st model to have electrons
15.
16.
Quantum
Mechanical Theory Modern
theory of the atom
17.
Worksheet # 11 Electron
Dot Diagrams
Draw structural and electron-dot
diagrams for each.
|
|
Structural |
Dot-Diagram |
|
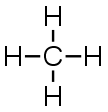
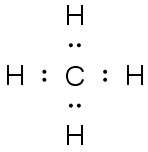
CH4 |
|
|
|
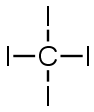
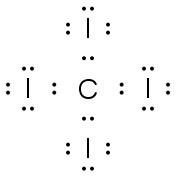
CI4 |
|
|
|
S2 |
|
|
|
P2 |
|
|
|
C2Cl6 |
|
|
|
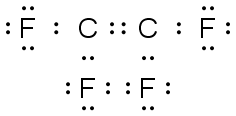
C2F4 |
|
|
|
NF3 |
|
|
|
CS2 |
|
|
|
N2Cl2 |
|
|
|
HCN |
|
|
|
CH4N2O (symmetrical) |
|
|
|
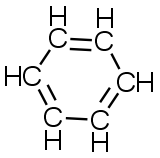
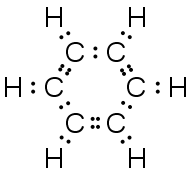
C6H6 (cyclic) |
|
|
|
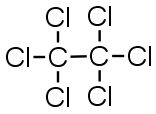
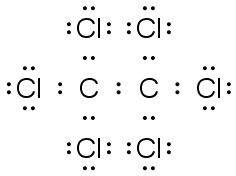
CF4 |
|
.. : F : .. .. .. : F
׃ C ׃ F : .. .. .. : F : .. |
|
N2Cl4 |
Cl
– N –
N – Cl | | Cl Cl |
|
|
NBr3 |
Br – N – Br | Br |
.. ..
.. : Br : N : Br : .. ..
.. : Br : .. |
|
N2 |
N ≡ N |
: N : : : N : |
|
O2 |
O = O |
.. .. : O : : O : |
|
I2 |
I - I |
.. .. : I : I
: .. .. |
|
CO2 |
O = C = O |
.. .. : O : : C : : O : |
|
COBr2 |
Br | O = C | Br |
.. : Br : .. : O : : C .. : Br : .. |
|
CNCl2F (symmetrical) |
|
.. : Cl: .. .. : F : C : : :N .. .. : Cl : .. |
Name each compound
1. CH3COOH(aq) Acetic or ethanoic acid
2. HBr(aq) Hydrobromic acid
3. HF(g) Hydrogen fluoride
4. HNO3(aq) Nitric
acid
5. HClO4(aq) Perchloric
acid
Write the quantum electron
configurations for the following.
6. Cl- 1s22s22p63s23p6
7. Sr2+ 1s22s22p63s2
3p63d104s24p6
8. I 1s22s22p63s2
3p63d104s24p64d105p5
Write a dissociation equation for
each to show how each ionizes in water.
9. CH3COOH(l) → H+(aq) +
CH3COO-(aq)
10. HNO3(l) → H+(aq) +
NO3-(aq)
11. Al2(SO4)3(s) → 2Al3+(aq) + 3SO42-(aq)
12. Co3(PO4)2(s) → 3Co2+(aq) +
2PO43-(aq)
Name each compound above.
13. Hydrogen acetate
14. Hydrogen nitrate
15. Aluminum sulphate
16. Cobalt II phosphate
17.
Classify the following compounds.
NaOH BaF2 BCl5 CH3COOH
H2CO3 CsOH S2Cl2 BaCl2
|
Salt |
Base |
Acid |
Covalent Nonacid |
|
BaF2 |
NaOH |
CH3COOH |
S2Cl2 |
|
BaCl2 |
CsOH |
H2CO3 |
BCl5 |
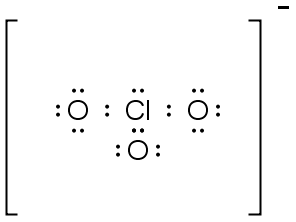
Worksheet # 12 Electron Dot Diagrams
Draw structural and electron-dot
diagrams for each.
|
ClO3- |
|
PO43- |
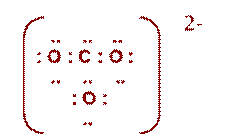
: O : ..
.. .. : O : P : O : .. ..
.. : O : .. |
|
IO3- |
-
: O : I : O : .. : O : .. |
BrO3- |
-
.. ..
.. : O :Br: O : .. ..
.. : O : .. |
|
CN- |
|
NO3- |
-
: O : N :: O : .. ..
: O : .. |
|
SO42- |
2-
: O : .. ..
.. : O : S : O : .. ..
.. : O : .. |
CaCO3 |
2+
Ca
|
|
Li2SO4 |
+
2 Li 2- ..
.. ..
.. : O : S : O : .. ..
.. : O : .. |
CCl4 |
.. : Cl : .. ..
.. : Cl ׃ C ׃ Cl
: .. ..
.. : Cl : .. |
|
NI3 |
.. ..
.. : I
׃ N ׃ I : .. ..
.. : I : .. |
NSCl |
.. ..
: Cl : N : : S : ..
|
|
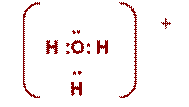
NH4+ |
H + .. H : N : H ..
H |
H3O+ |
|
|
NaCl |
+ −
: Na : : Cl : .. .. |
ClO3- |
|
Draw structural and electron-dot
diagrams for each.
|
BrO4- |
3-
: O : .. .. .. : O : Br : O : .. : O : .. |
PO33- |
3-
: O : .. .. .. : O : P : O : .. |
|
IO4- |
-
: O : .. .. .. : O : I : O : .. ..
.. : O : .. |
NO3- |
: O : .. .. .. : O : N : : O : .. |
|
HCN |
H : C : : : N : |
SO32- |
2-
: O : .. .. .. : O : S : O : .. ..
.. |
|
CO32- |
|
CaS |
2+
Ca 2-
: S : .. |
|
Na2SO4 |
2 Na
2-
: S : .. |
NCl3 |
|
|
N2 |
|
O2 |
.. .. : O : : O : |
|
Cl2 |
.. .. : Cl : Cl : .. .. |
C2H6 |
|
|
C2H4 |
|
C2H2 |
|
Draw electron dot diagrams for each
ionic compound
|
LiCl |
.. [ Li ]+ [ :Cl:
]-
..
|
|
Na2O |
[ Na ]+ [ :O: ]2- [ Na ]+
.. |
|
K2S |
.. [K ]+ [ : S : ]2- [ K ]+
.. |
|
BaO |
.. [ Ba ]2+ [ :O: ]2-
.. |
|
GaH3 |
[ H: ]- [ H: ]- [ Ga ]3+ [ H: ]-
|
Worksheet
# 13 Practice
Test # 1
1. Classify
as stable or reactive.
Na N+ Ne Cl- S2- S3-
P P3- Ca Ca2+ NaCl N3-
2. Describe
a metal and a nonmetal in terms of gaining or losing electrons.
Metals lose electrons and
nonmetals gain electrons.
3. Why
are noble gases always stable?
Full outer shells
4. Determine
the number of valence electrons for:
Ca 2 Ca2+ 8 Cl 7 Cl- 8
O 6 O2- 8 Al 3
5. Draw
a Bohr diagram for
Ca Ca2+
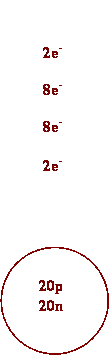
6. Determine
the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in each.
|
|
Protons |
Neutrons |
Electrons |
|
S |
16 |
16 |
16 |
|
S2- |
16 |
16 |
18 |
|
Al |
13 |
14 |
13 |
|
Al3+ |
13 |
14 |
10 |
|
42Ca |
20 |
22 |
20 |
7. Classify
as ionic or covalent
compounds.
HCl CH3OH H2O NH4OH
NaCl MgSO4 CoCl2 H3PO4
NH3 P2O5 Ba(OH)2
8. Classify
the above compounds into acids, non-acids, salts and bases.
Acids H3PO4 HCl
Bases NH4OH Ba(OH)2
Non-acids H2O NH3
Salts MgSO4 NaCl
9. Calculate
the average atomic mass for magnesium using the following percentage abundance
data.
24Mg 78.70%
(24.00 amu)
25Mg 10.13% (25.00
amu)
26Mg 11.17%
(26.00 amu)
0.7870(24.00) + .1013(25.00) + .1117(26.00)
= 24.32 amu
10. Write
the formulas for each ionic compound.
Magnesium chloride MgCl2
Silver phosphate Ag3PO4
Cobalt III oxide Co2O3
Zinc phosphate Zn3(PO4)2
Calcium nitride Ca3N2
Copper I nitrate CuNO3
11. Name
each ionic compound.
Fe2(SO4)3 iron III sulphate CoCl3 col
Na2O sodium
oxide AgCl
Na3PO4 sodium phosphate CaF2
NH4OH
ammonium
hydroxide Ca(NO3)2
K2Cr2O7 potassium dichromate MgCrO4
12. Name each covalent compound.
P2O5 diphosphorus pentoxide N2O3 dinitrogen
trioxide
CO carbon
monoxide CO2 carbon dioxide
SO2
sulphur dioxide P3O5
triphosphorus pentoxide
C6H6 hexacarbon hexahydride H2SO4(l) hydrogen
sulphate
HCl(l) hydrogen chloride HNO3(l) hydrogen nitrate
H2CrO4(aq) chromic acid HF(aq) hydrofluoric
acid
H3PO4(l) hydrogen
phosphate H2CO3(aq) carbonic acid
13. Complete the chart below.
|
|
Protons |
Neutrons |
Electrons |
Reactive or stable? |
# of valence electrons |
|
Li+ |
3 |
4 |
2 |
stable |
2 |
|
S2- |
16 |
16 |
18 |
stable |
8 |
|
22Mg2+ |
12 |
10 |
10 |
stable |
8 |
14. Write
dissociation equations showing how each salt or acid dissolves in water and
forms ions. The first one is done for you.
MgCl2 → Mg2+ +
2Cl-
FeCl3 → Fe3+ +
3Cl-
Co2(SO4)3 → 2Co3+ +
3SO42-
HClO3
→ H+ +
ClO3-
H2Cr2O7 → 2H+ +
Cr2O72-
16. Name
each acid:
HCl(aq) hydrochloric acid HClO3(aq) chloric acid
HNO3(aq) nitric acid HBr(aq) hydrobromic
acid
17. Classify
each as formula units or molecules.
NaF H2O
CH4 NH4Cl
Ionic compounds start
with metals and have formula units.
Covalent
compounds start with nonmetals and have molecules.
CaSO4 CH3OH
H2SO4
18. Indicate
the solutions that conduct
electricity.
NaCl(s) solid NaCl(aq)
Ca(OH)2(aq) HCl(aq)
NH4OH(aq)
C6H12O6(aq)
19. Consider the following electron configuration 1s22s22p6.
Determine the element and
some ions that have the above
electron configuration.
Element Ne
Cation Na+
or Mg2+
Anion F- O2- N3-
20. Describe
why NaCl(s) doesn’t conduct
electricity. Describe what happens to
NaCl(s) when it is dissolved in
water. Why does it conduct electricity?
The ions in NaCl(s) are not free to move and conduct
electricity.
When
it is dissolved in water, the NaCl dissociates into
ions that conduct electricity.
NaCl(s) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
21. Write
the quantum electron configuration for each (1s22s2p.....)
He 1s2 Ar 1s22s22p63s23p6
Na 1s22s22p63s1 Na+ 1s22s22p6
Cl 1s22s22p63s23p5 Cl- 1s22s22p63s23p6
K 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 K+ 1s22s22p63s23p6
Br 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p5 Br- 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p6
22. What two particles make up most of the mass within an atom? Protons and neutrons.
23. I am
an atom with 35p 40n. Who am I? Br
24. I am
a cation with 56p
81n & 54e.
Who am I? Ba2+
25. Define
isotopes. Elements
that have the same atomic number but different
atomic mass because of having different
amounts of neutrons.
26. In
un-deflected and others were radically
deflected. Describe the significance of each in terms of the structure of the
atom.
There is a small dense
positive nucleus in the center of the atom with most of the mass.
27. Define
ionic and covalent bonding.
Ionic bonding transfers an
electron from the metal, which becomes a cation to
the nonmetal,
which becomes the anion.
Covalent bonding occurs between two
nonmetals and involves shared electrons.
28. How
many valence electrons are in the calcium ion?
8
29. How
many valence electrons are in the fluoride ion?
8
30. What is
the name of the family that has and electron configuration of:
a) s2p5
Halogens
b) s1 Alkali Metals
c) s2p2 Carbon Family
31. Consider the following electron configuration 1s22s22s22p63s23p6
. Determine the element and some ions that have the above electron configuration. These are called
isoelectronic.
Element: Ar
Cations: K+ Ca2+
Anions: Cl- S2- N3-
Draw electron dot diagrams
for the following using brackets for ions. Write a dissociation equation first.
32. NaCl
..
[ Na ]+ [ :Cl: ]-
..
33. Li2O
..
[ Li ]+ [ :O: ]2- [ Li ]+
..
34. CaF2
.. ..
[ :F: ]- [ Ca ]2+ [ :F: ]-
.. ..
Name and classify each
compound as an acid, molecular, salt, or base.
35. CuSO4(aq) Salt Copper II sulphate
36. P2O4(s) Molecular Diphosphorus tetroxide
37. H2SO4(aq) Acid Sulphuric acid
38. H2Cr2O7(aq) Acid Dichromic
acid
39. H2Cr2O7(l) covalent
nonacid
Hydrogen dichromate
40. Ca(OH)2 .
5H2O Base Calcium hydroxide pentahydrate
41. HBr(aq) Acid Hydrobromic
acid
42. Calculate the average atomic mass for neon if there are three
naturally occurring isotopes and they are:
20Ne mass = 19.9924404 amu abundance = 90.92 %
21Ne mass = 20.993849 amu abundance = 0.2570 %
22Ne mass = 21.991385 amu abundance = 8.820 %.
Show some work if you want some marks.
Round to an appropriate number of sig figs.
0.9092(19.9924404)
+ 0.002570(20.993849) + 0.08829(21.991385) = 20.17 amu
Ca(OH)2 calcium hydroxide NH4OH ammonium hydroxide
CH3OH methanol C12H22O11 sucrose
HCl hydrochloric acid PI3 phosphorus triiodide
K2SO4 potassium sulphate RbOH rubidium hydroxide
H3PO4 phosphoric acid NaOH sodium hydroxide
CaCl2 calcium chloride Li2SO4 lithium sulphate
SiO2 silicon dioxide BaF2 barium fluoride
BCl5 boron pentachloride CH3COOH acetic acid
H2CO3 carbonic acid CsOH cesium hydroxide
S2Cl2 disulphur dichloride Fr2S francium sulphide
Fe2(SO4)3 iron (III) sulphide ZnCl2 zinc chloride
Co3(PO4)2 cobalt (II) phosphate Ag2Cr2O7 silver dichromate
Worksheet # 14 Practice
Test
# 2
Balance
each equation.
1. 2C16H34 + 49O2 → 32CO2 + 34H2O
2.
2Ga +
3H2SO4 → 3H2 + 1Ga2(SO4)3
Write
a balanced equation including phase symbols.
3.
Solid carbon reacts with chlorine
gas to produce liquid tetracarbon decachloride.
4C(s) + 5Cl2(g) →
C4Cl10(l)
Write
chemical formulas for each ionic or molecular compound.
4.
Strontium sulphide SrS
5.
triphosphorous hexoxide P3O6
6. Osmium
IV sulphide OsS2
Name
each chemical formula
7.
Sn(CO3)2.5H2O Tin IV carbonate pentahydrate
8.
Si3F8 Trisilicon octafluoride
9.
NaHCO3 Sodium bicarbonate
Classify
the following as acids, bases, salts, and molecular non-acids. Name each.
10.
Sn(SO4)2 Salt Tin
IV sulphate
11.
Ca(OH)2 Base Calcium hydroxide
12.
CH3COOH Acid Acetic Acid
13.
S2O5 Molecular Disulphur pentoxide
Round
off each measured number to three significant figures.
14.
0.0056349 0.00563
15.
539663 540000 or 5.40 x 105
Add
or subtract the measured quantities.
16.
153.267 +
0.53493 153.802
17 ( 4.5631 x
1024 ) ( 2.36
x 10- 23 ) 108
Simplify
the following rounding to the correct number of significant figures.
18.
(5.6 x 10 -24) (5.37894 x 10-25)(6.532 x 1015) = 1.9 x 10-67
(2.059378 x 1024)(5.23 x 1022)(9.37894 x 10-13)
Use
unit analysis and the conversion factors to perform the following conversions:
2.210
lb = 1.000 kg 14
lb = 1 stone (defined)
2000
lb = 1 ton (defined) 1.61 km = 1.00 mile
4.54
L = 1.00 gallon 16
oz =
1 lb (defined)
19.
236 oz to stone
236
oz x 1 lb x 1 stone = 1.05
stone
16 oz 14 lb
20.
8.53 stone to oz
8.53
stone x 14 lb x 16
oz = 1.9 x 103 oz
1 stone
1 lb
21.
25.6 mi/h to km/s
25.6
mi x 1.61 km x 1
h = 0.0114 km/s
h 1.00 mi 3600s
State
the model of the atom is best described by each statement below.
22. First
model to account for The Law of Conservation of Mass.
23.
The first theory to explain the
emission of photons. Bohr
24. First
model to account for positive and negative charges. Thomson
25. First
model to account for the wave properties of electrons. Quantum
26. First
model to include a small dense nucleus.
27.
Describes the atom as a small dense
nucleus surrounded with electrons, which are not in orbitals.
28.
Describes the atom as a small dense
nucleus surrounded with electrons, which are in spherical orbitals.Bohr
29.
Describes the atom as a spherical atom
that is indestructible and combines in simple whole number ratios to form compounds.
30.
Describes electrons as being contained
in a complex 3D orbitals as
negative clouds of vibrational energy. Quantum
31.
Non-scientific theory that delayed
modern theories of the atom for 1800 years and was shown to be incorrect. Aristotle’s
What
did the evidence tell us about the nature of the atom?
32.
99 % of alphas in the gold foil
experiment were completely un-deflected.
Most of
the atom is empty space.
33.
1 % of alphas in the gold foil
experiment were radically deflected.
There is
a small dense positive nucleus.
34.
Flame spectroscopy of an element
produces an emission spectrum consisting of 4 photons.
Electrons
are in orbitals
35. A beam of negative particles is produced in
a Crooke’s tube.
There
are electrons.
36. There
are five naturally occurring isotopes of Germanium. Complete the chart to show
the number of protons neutrons and electrons.
protons neutrons electrons At. Mass
Abundance
70Ge 32 38 32 69.92428 20.52%
72Ge 32 40 32 71.92174 27.43%
73Ge 32 41 32 72.9234 7.760%
74Ge 32 42 32 73.92115 36.54%
76Ge 32 44 32 75.9214 7.760%
37. Calculate
the average atomic mass of Germanium. Show some work if you want some marks. Round to an appropriate number of significant figs.
0.2052(69.92428) + 0.2743(71.92174) +
.07760(72.9234) + 0.3654(73.92115) +
.07760(75.9214) = 72.64 amu
38.
Write the quantum electron
configurations for the following atoms or ions.
39.
F 1s22s22p5
40.
Ga 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p1
41.
Br- 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p6
42.
Rb+
1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p6
Determine
the element that has the following electron configuration.
43. 1s22s22p63s2 Mg
Determine
a cation that has the following electron configuration.
44.
1s22s22p63s23p6 K+ Ca2+ Ga3+
Determine
an anion that has the following electron configuration.
45.
1s22s22p63s23p6 P3- S2- Cl-
Complete
the following chart.
Symbol p e n valance
el. stable/unstable atom/cation/anion
46.
Na 11 11 12 1 unstable atom
47.
P-3 15 18 16 8 stable anion
48.
Xe 54 54 77 8 stable atom
49.
Sr+2 38 36 50 8 stable cation
Name
and classify each compound as an acid, molecular, salt, or base.
50. CuSO4(aq) Salt Copper
II sulphate
51. P2O4(s) Molecular Diphosphorus tetroxide
52.
H2SO4(aq) Acid Sulphuric acid
53.
H2CO3(aq) Acid Carbonic
acid
54.
H2CO3(l) Nonacid
Covalent Hydrogen
carbonate
55. Ba(OH)2. 2H2O Base Barium
hydroxide dihydrate
56.
HF(aq) Acid Hydrofluoric
acid
Write
structural diagrams and electron-dot diagrams for each.
57. CCl4
..
: Cl :
..
.. ..
: Cl
׃ C ׃ Cl :
.. .. ..
: Cl :
..
58. S2
..
..
: S :
: S :
59. NH3
..
H : N : H
..
H
60. CO2
.. ..
: O :
: C : : O :
Write
electron-dot diagrams for each.
61. NaCl
.. ..
[ : Na : ]+ [ : Cl : ]-
.. ..
62. SO42-
2-
..
 : O :
: O :
.. .. ..
: O : S : O :
.. .. ..
: O :
..
63. Na3PO4
64. NO3-
 ..
.. -
..
.. -
: O : N :: O :
..
..
: O :
..
65. NH4+
66. IO4-
-
 ..
..
: O :
.. .. ..
: O : I : O :
.. .. ..
: O :
..