Unit 1 Safety, Review and Measurement

Lesson Day Date Topic Homework
1. Safety Assignment # 1
2. Review Assignment # 2
3. Balancing Equations
Assignment # 3
4. Formulas
Equations Assignment # 4
5. Measurement and
Uncertainty
6. Uncertainty Lab Day 1
7. Uncertainty Lab Day 2
8. Significant Figures Assignment # 5
9. Unit Analysis 1 Assignment # 6
10. Unit Analysis 2 Assignment # 7
11. Review Assignment # 8
12. Practice
Test Assignment # 9
Assignment # 1 Safety and Review
Complete the safety map for the room by indicating the
location of the fire extinguishers, doors, eyewash, ,
fire blanket, ,
eye-goggles, broken glass container, soap
dispensers, paper towel
dispensers, and soap sprayers. This is like a treasure hunt.
Get up and look for everything.
Room #
Ionic
Formulas
Write the ionic
formula, name, and dissociation equation for each combination
indicated by the cell below.
Note that all
ionic compounds (start with metals) are solids at room temperature.
*For those that start with H
(covalent compounds) the two largest formulas are solids, the
next three larger formulas are liquids, and the three smallest
are gases.
The last one,
which you can drink, is a liquid.
|
|
Li |
Mg |
Al |
NH4 |
Na |
Ba |
K |
Ca |
*H |
|
OH |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
|
SO4 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
|
Br |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
|
F |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 |
|
NO3 |
37 |
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 |
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 |
|
PO4 |
46 |
47 |
48 |
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 |
53 |
54 |
|
S |
55 |
56 |
57 |
58 |
59 |
60 |
61 |
62 |
63 |
|
C2O4 |
64 |
65 |
66 |
67 |
68 |
69 |
70 |
71 |
72 |
|
Cr2O7 |
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 |
77 |
78 |
79 |
80 |
81 |
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
59.
60.
61.
62.
63.
64.
65.
66.
67.
68.
69.
70.
71.
72.
73.
74.
75.
76.
77.
78.
79.
80.
81.
Chemical
Equations from Word Equations
1. Aqueous
potassium hydroxide is reacted with aqueous sulphuric acid producing a solution
of potassium sulphate and water.
2. Sodium
metal is reacted with zinc iodide in solution.
The products obtained are aqueous sodium iodide in and zinc metal.
3. Solid
calcium sulphate dihydrate is added to gaseous sulphur trioxide producing solid
calcium sulphate and aqueous sulphuric acid.
4. Solid
calcium phosphate and aqueous sodium nitrate are formed when solutions of
sodium phosphate and calcium nitrate are mixed.
Assignment # 2 Physical Chemical Changes Balancing
Equations
Classify as a physical or chemical
change.
1. Spoiling of food
2. Vaporization of ice
3. Stretching of a rubber band
4. Dynamite explosion
5. Shattering of glass
6. Decaying of dead bodies
7. Extraction of iron from form (Fe2O3)
8. Spontaneous combustion of oily rags
9. Grinding of wheat
10.
Melting snow
11. 2 H2O →2 H2 + O2 +
Energy
12. E
+ NaCl(s) →
NaCl(aq)
13. Determine the physical state of each
element at -5 0C (use the Handbook,
Textbook, or Internet to determine the melting point and boiling point of each).
mp bp physical state
a)
Mercury
b)
Bromine
c)
Chlorine
Classify as a physical or chemical
properties.
14. Sugar chars when heated
15. Yellow color of sulphur
16. Tarnishing ability of sulphur
17. Flexibility of a spring
18. Thermal conductivity of iron
19. Hardness of a diamond
20. Stability of nitrogen
21. Describe 11 and 12 as exothermic or
endothermic
Write Ionic Formulas
22. Aluminum oxide
23. Aluminum chloride
24.
Ammonium acetate
25.
Barium phosphate
26. Calcium hydroxide
27.
Sodium hydroxide
28. Strontium phosphate
29. Iron II phosphate
30. Cobalt III sulphate pentahydrate
31. Copper II nitrate hexahydrate
Write a balanced equation and
include all phase symbols
32. Sodium chloride dissolving in water
(endothermic).
33.
Lead II nitrate reacting with sodium
phosphate to produce solid Lead
II phosphate and sodium nitrate (exothermic and three chemicals are aqueous).
34. List three chemical and physical
properties.
Assignment # 2 Classifying Matter And Balancing
Equations
1. Label each as chemical or physical.
a)
Ice cubes turn to water
b)
Steam forms water droplets in a
mirror
c)
Milk is made into ice milk
d)
Ice cubes shrink in a freezer
e)
Perspiration “dries”
f)
Bromine is liquefied from solid bromine
2. What change in physical state occurs
during the formation of the following?
a) Rain
b) Snow
c) Frost
d) Steam
3)
A sealed glass bulb is half-filled
with water, on which some ice and wood
are floating. The remainder of the bulb
is filled with air. How many physical states are
present? Identify them.
4) Classify each of the following as a
physical or chemical change.
a)
Photosynthesis (CO2+H2O→Sugar+oxygen)
b) Antifreeze boils out of a radiator
c) A firefly emits light
d)
A nail is magnetized
e) A nail rusts
f) Leaves turn color in autumn
g)
Food spoils
h) Dynamite explodes
I) Grinding of wheat into flour
j) Shattering of glass
k) Extraction of iron from iron ore (Fe2O3)
5) Identify the chemical and physical
changes in the following sequences:
a)
A lump of sugar is ground to a
powder and then heated in air . It melts ,
then darkens ,
and finally bursts into flames and burns .
b)
Gasoline is sprayed into the
carburetor ,
mixed with air , converted to vapor , burned , and the combustion
products expand the cylinder .
6. Classify the following as elements,
compounds, or mixtures:
a)
Methane (CH4)
b)
Pizza
c) Milk shake
d) Zinc
e) Laughing gas
f)
Clean air
g) Chocolate chip cookie
7. A pure blue powder when heated in a
vacuum releases a greenish colored gas
and leaves behind a white solid. Is the
original blue powder a compound or
element? Explain.
8. A shiny, metallic-like substance
conducts an electric current without a change
in its properties. The substance is
heated until it liquefies and then
an electric current is passed through the liquid again without a change in properties. Is the substance likely to be an element or compound? Explain.
9. Describe the difference between
chemical and physical change in terms of
what occurs with the atoms involved.
Balancing
Equations
1. ___KNO3 → ___KNO2 + ___O2
2. ___CaC2 + ___O2 → ___Ca + ___CO2
3. ___C5H12 + ___O2 → ____CO2 + ___H2O
4. ___K2SO4 + ___BaCl2
→ ____KCl + ___BaSO4
5. ___KOH + ___H2SO4 → ____K2SO4 + ___H2O
6. ___Ca(OH)2 + ___NH4Cl → ____ NH4OH + ___CaCl2
7. ___C + ___SO 2
→ ___CS2 + ___CO
8. ___Mg3N2 + ___ H2O → ____
Mg(OH)2 + ___NH3
9. ___V2O5 + ___Ca → ___CaO + ___V
10. ___Na2O2 + ___H2O → ____NaOH + ___O2
11. ___Fe3O4 + ___H2
→ ____Fe + ___H2O
12. ___Cu + ___H2SO4 → ____CuSO4 +
___H2O +
___SO 2
13. ___Al + ___H2SO4 → ____ H2 + ___
Al2(SO4)3
14. ___Si4H10 + ___O2 → ___SiO2 + ___H2O
15. ___NH3 + ___O2 → ___N2H4 + ___H2O
16. ___C15H30 + ___O2 → ___CO2 + ___H2O
17. ___BN + ___F2 → ___BF3 + ___N2
18. ___CaSO4 . 2 H2O +
___SO3 → ___CaSO4 + ___H2SO4
19. ___C12H26 + ___O2 → ___CO2 + ___H2O
20. ___C7H6O3 + ___O2 → ___CO2 + ___H2O
21. ___Na + ___ZnI2 → ___NaI + ___NaZn4
22. ___LiAlH4 + ___BF3 → ___LiF +
___AlF3 + ___B2H6
23. ___HBrO3 + ___HBr → ___H2O + ____Br2
24. ___O2 +
___All4C3
+ ___H2O → ___Al(OH)3 +
___CH4
25. ___Ca(NO3)2
. 3H2O + ___LaC2 → Ca(NO3)2 +
___La(OH)2 + ___C2H2
26. ___CH3NO2 +
___Cl2 →
___CCl3NO2 +
___HCl
27. ___Ca3(PO4)2 +
___SiO2 + ___C
→ ___CaSiO3 +
___CO + ___P
28. ___Al2C6 +
___H2O → ___Al(OH)3 +
___C2H2
29. ___NaF +
___CaO + ___H2O → ___CaF2 +
___NaOH
30. ___LiH +
___AlCl3 → ___LiAlH4 + ___LiCl
31. ___CaF2 +
___H2SO4 +
___SiO2 →
___CaSO4 + ___SiF4 +
___H2O
32. ___CaSi2 +
___SbCl3 → ___Si
+ ___Sb +
___CaCl2
33. ___TiO2 +
___B4C + ___C
→ ___TiB2 +
___CO
34. ___NH3 + ___O2 → ___NO +
___H2O
35. ___SiF4 + ___NaOH
→ ___Na4SiO4 +
___NaF + ___H2O
36. ___NH4Cl + ___CaO
→ ___NH3 +
___CaCl2 + ___H2O
37. ___NaPb + ___C2H5Cl → ___Pb(C2H5)4 +
___Pb + ___NaCl
38. ___Be2C + ___H2O → ___Be(OH)2 +
___CH4
39. ___NpF3 +
___O2 + ___HF
→ ___NpF4 +
___H2O
40. ___NO2 + ___H2O → ___HNO3 +
___NO
Some Tough
Ones
___FeCl2 +
___KNO3 + ___HCl
→ ___FeCl3 + ___NO
+___ H2O + ___KCl
___Cu + ___HNO3 → ___Cu(NO3)2 +
___NO + ___H2O
___ KMnO4 + ___ HBr
→ ___MnBr2 +
___Br2 + ___KBr
+ ___H2O
___ K2Cr2O7 + ___HCl
→ ___KCl
+ ___CrCl3 +
___H2O + ___Cl2
Assignment
# 3 Balancing Equations
1. ___Al + ___HCl → ___AlCl3 + ___H2
2. ___Zn + ___KOH → ___K2ZnO2 + ___H2
3. ___B2O3 + ___Mg → ___MgO + ___B
4. ___C6H11OH + ___O2 → ___H2O + ___CO2
5. ___C12H26 + ___O2 → ___HOH
+ ___CO2
6. ___Na + ___H2O → ___NaOH + ___H2
7. ___PbS + ___O2 → ___PbO + ___SO2
8. ___SiCl4 + ___Na → ___Si + ___NaCl
9. ___Mg + ___CO2 → ___MgO + ___C
10. ___Al + ___H2SO4 → ___Al2(SO4)3 +
___H2
Write Formulas for each
11. Zinc phosphate
12. Ammonium carbonate
13. Iron III oxalate
14. Copper II tripolyphosphate
pentahydrate
15. Cobalt II borate
16. Triphosphorus tetroxide
17. Dicarbon hexachloride
18. Trisilicon octafluoride
19. Sodium tetraborate
20. Aluminum dichromate
21. Calcium oxide
22. Silver thiosulphate
Write balanced chemical equations and include phase symbols
for each formula.
23. Aqueous
calcium nitrate is reacts with a solution of sodium phosphate producing solid calcium phosphate and aqueous
sodium nitrate.
24. Gaseous
nitrogen trihydride reacts with oxygen gas to produce gaseous nitrogen monoxide and gaseous water and
energy.
25. Phosphoric
acid reacts with Calcium hydroxide both in solution to produce and aqueous salt and water.
26. Write
an equation for the combustion of sucrose.
27. Write
an equation for the cellular respiration of vitamin C.
28. Describe
what you know about covalent or molecular compounds.
Worksheet # 4 Balancing
Equations Naming Formulas
1. ___Sb + ___Cl2 → ___SbCl5
2. ___FeCl2 + ___Cl2 → ___FeCl3
3. ___P + ___I2 → ___PI3
4. ___Na2S + ___HCl → ___NaCl + ___H2S
5. ___NaOH + ___FeCl3 → ___NaCl + ___Fe(OH)3
6. ___KOH + ___H3PO4 → ___K3PO4 + ___H2O
7. ___NaOH + ___CuSO4 → ___Na2SO4 + __Cu(OH)2
8. ___HNO3 + ___Ca(OH)2 → ___H2O + __Ca(NO3)2
9.
___NH3 + ___CuO → ___H2O +
___Cu + ___N2
10. ___N2 +
___C +___Na2CO3 → ___NaCN +
___CO
11. ___NH3 + ___O → ___NO + ___H2O
12. ___NH3 + ___O2 → ___NO2 + ___H2O
13. ___NH3 + ___O2 → ___N2O5 + ___H2O
14. ___P + ___N2O → ___P2O5 + ___N2
15. ___Al + ___HCl → ___AlCl3 + ___H2
16. ___Zn + ___KOH → ___K2ZnO2 + ___H2
17. ___B2O3 + ___Mg → ___MgO + ___B
18. ___CH3OH + ___O2 → ___H2O + ___CO2
19. ___C6H12O6 → ___C2H5OH +
___CO2
20. ___Na + ___H2O → ___NaOH + ___H2
21. ___PbS + ___O2 → ___PbO + ___SO2
22. ___SiCl4 + ___Na → ___Si + ___NaCl
23. ___Mg + ___CO2 → ___MgO + ___C
24. ___Al + ___H2SO4 → ___Al2(SO4)3 +
___H2
Write balanced chemical formulas for each ionic compound.
25. Calcium
hydroxide
26. Aluminum
sulphate
27. Iron
III oxide
28. Zinc
acetate
29. Barium
carbonate
30. Sodium
phosphate
31. Cobalt
II nitride
32. Gallium
sulphate
33. Aluminum
fluoride
34. Ammonium
sulphate
35. Aluminum
acetate
Write balanced chemical formulas for each molecular
(covalent) compound.
36. carbon
monoxide
37. dinitrogen
tetraiodide
38. triphosphorus hexafluoride
39. dinitrogen dioxide
Write balanced chemical equations for each word equation.
Include phase symbols for all formulas.
40. Solid
sodium oxide dissolves in water to make sodium oxide solution.
41. Solid
aluminum sulphate dissolves in water to make a solution
42. Barium
phosphate plus sodium sulphate (both in water) yields solid barium sulphate and aqueous sodium phosphate.
43. Lead
metal added to Sulphuric acid solution produces lead IV sulphate precipitate and diatomic hydrogen gas.
44. Potassium
iodide (aq) plus lead II nitrate (aq) yields potassium nitrate (aqueous) plus lead II iodide (solid).
45. Calcium
carbonate (solid) plus aqueous hydrochloric acid yields (aqueous) calcium chloride, carbon dioxide gas
and water.
46. Potassium
nitrate (aq) plus iron III hydroxide (aq) yields iron II nitrate (aq) plus potassium hydroxide (aq).
You are good if you can do these.
1. ___HCl +
____K2CrO4
→ ____KCl + ____CrCl3 +____H2O +____Cl2
2. __K2Cr2O7 +
__KI + __H2SO4 → __K2SO4 + __Cr2(SO4)3 +
___I2 +___H2O
Worksheet # 5 Measurement
and Uncertainty
1. Five
different voltmeters are used to measure the voltage in a circuit. Determine the average and uncertainty.
25.61V
25.63V
25.65V
25.64V
25.63V
Six
thermometers give the following readings. Determine the average and the
uncertainty.
352.4 0C
352.5 0C
352.6 0C
352.5 0C
352.7 0C
352.6 0C
2. Determine
the average and uncertainty for the data:
25.56
g 25.54g 25.52g 25.53g 25.55g
Answer
3. Determine
the average and uncertainty for the data:
5.216
oC 5.218 oC 5.213 oC 5.214 oC 5.416 oC
Answer
4. How
many significant figures are in each number?
25.63 101 0.0075
0.0002 1.00 2.005
10.031 1.0002 10005
0.00521 2.51 x 104 3 x 10-7
2
x 105 2.00
x 103 250.
5. Round
off to three significant figures.
0.05211 0.0087251
85.337 2.6177 x 10-5
2.5175
x 10-18 25.731 x 105
Round
off each measured number to three significant figures.
6. 0.002567
7. 94549
8. 15.00
9. Round
off the following numbers to three significant figures:
a) 35.234 b) 2.34521
c) 0.035219 d) 2533521
e) 6255520000
10. State
the number of significant figures in each approximate number.
a) 305 b)
25.25
c) 3.00 d)
0.001
e) 3.0050 f) 6.25
x 1023
g) 7.00
x 10-2 h) 1001
11. Add
or subtract the measured quantities.
25.31
22.0 22.7 35.271
+ 6.4 + 0.04 +
0.77 +
0.2
22.71 25.217 2.51639 8.0558
-
0.299 + 0.017 - 1.2358 + 0.3259297
25.634 +
2.365 - 0.25498
+ 0.225 =
12.
15.239 + 5.36
13. 2.6679 -
1.23
14. 2.059378 x 1024 +
5.3 x 1022
15. 8.5 x 10 -24 +
5.37894 x 10-25
16. 2.3 x 10 16 +
8.224 x 1019
17. 5.6 x 10 –8 +
9.5563 x 10-6
18. 9.55 x 10 -10 +
5.4455 x 10-12
19. 2.66 x 10 -16 +
3.445 x 10-18
Assignment # 6
1. 25 x 3
2. 3.35
x 0.26
3.
799 x 877
4. (6.2
x 103)( 3.55 x 1012)
5.
(6.3 x 107)(2.51 x 10-7)
(3.214 x 10-5)
6. (7.52
x 1016)(3.1 x 1012)
7. 3.5
x 102 ÷ 3.1 x 103
(2.5 x 10-7)
8. (2.00
x 1023)(3.51 x 10-22)(3.5 x 103)
(7.5
x 10-3)(3.511 x 1012)(6.6 x 10-6)
9.
(5.200 x 10-5)(6.02
x 10-12)(3.58 x 1017)
(2.337
x 10-3)(6.2154 x 1012)(5.22 x 10-12)
10.
156 x
256 x 21
x 0.0005687
0.02569 x 13.235
x 2654
11.
(8.5 x 10 -24) ( 5.37894
x 10-25) ( 4.532
x 1015)
(2.059378
x 10 24) (5.3
x 1022) ( 9.37894
x 10-13)
12. 25.7
x 0.21
13. 35
x 105
14. 51.71
x 22.3
15. 22
x 305
16. Write
three examples of exact numbers.
17. Write
three examples of approximate numbers.
Circle the uncertain digit and
underline the uncertainty in each of the following numbers.
18. 35.2
± 0.1 g 19.
22.221 ± 0.005 mm 20.
100. ± 2 lb.
21. Give
the largest and smallest value of the approximate number
35.21
± 0.02 g
22. 26.215 23. 65.222 24. 22
- 0.01
-
0.3 +
1.03
25. 10.
+ 0.1 25. 33.3
+ 0.35 27.
29.39 + 0.2
Calculate
the average measurement and the uncertainty of each measuring device below:
29.
The mass (in grams) readings on a
balance:
58.56 g
58.59 g
58.51 g
58.61 g
58.57 g
58.56 g
Answer
30.
The voltage (in mV) readings on a
number of voltmeters:
123.2
124.5
124.0
124.3
124.3
Answer
31.
State the number of significant
digits for each number:
a) 0.00200
L b) 5.000
g
c) 1.00003
A d)
1000.000 Mm
e)
2.5 x 1076 f)
78.89 m
32.
Perform the following calculations
and round to the appropriate level of
uncertainty (assume all numbers are from measurements):
a) 18.
+ 0.21
b) 62.1 x
3021.56
c) 1.05
g + 253.8 mg + 24.98 mg Watch units!
d) (9.442
x 10-3)(3.21 x 108)
e) 231.4 -
8.2295
f) (8.995
x 106) + (3.55 x 107)
g) 12.0355
+ 1.024
h) (4.56
x 10-8)(2.5 x
1035)
i) (9.24
x 1010)(5.233 x
104)
33.
State the difference between
accuracy and precision.
Worksheet # 7 Unit Analysis 1
1. 527 g to mg
2. 1.05
x 106 um to m
3. 2.148 ML to mL
4. 0.0235 mg to kg
5. 8.32
x 10-4 mL to ML
6. 772.5 us to ms
7. 3.06500 cg to Kg
8. 9.450 Mm to mm
9. 5.64
x 103 mm2 to cm2
Non-metric/Metric
Conversions
Given that: 2.210 lb = 1.00
kg 4.54
L = 1.00 Gal
1.000 atm =
101.3 kPa 1.61 km = 1.00 mile
14 lb = 1
stone 2000
lb = 1 ton
16 oz = 1 lb
10. 170. lb to kg
11. 648 kPa to atm
12. 256 oz to tons
13. 0.025 ton to mg
14. 0.236 Gal to mL
15. 5.8 x 106 mL to Gal
16. 5.66 x 106 mg to stones
17. 15 miles to mm
18. 5.63 x 109 µm to miles
Worksheet # 8 Unit Analysis 2
1. 605 µm
to mm
2. 6.5
x 10-6 Mm to
m
3. 20.0 Km
to cm.
4. 8.774
x 1015 µm to Mm.
5. 25 cL
to ML
6. 648 KPa
to mPa
7. 2.665 Mg
to µg
Use unit
analysis and the conversion factors to perform the following conversions:
2.210 lb =
1.000 kg 14 lb = 1 stone (defined) 2000 lb = 1 ton (defined)
1.61 Km =
1.00 mile 4.54 L = 1.00
gallon 16 oz = 1 lb
(defined)
8. 152 mL to gal
9. 8.6
stone to oz
10. 4.3 m to miles
12. 15.2 mi/gal to L/km
13. 2.3
gal to mL
14. 45.2
oz to stones
15. 46.3 miles to m
16. 36 L/km to mi/gal
17. If 3 dogs are worth 2 cats, 8 cats are
worth 2 lions, 5 lions are worth 8 elephants, 2 elephants are worth 8700000 ducks, 47 ducks are worth 63
geese, 14 geese are worth 27
snakes, 42 snakes are worth 778396 fruit flies, and a dog costs $205.00, how
much does a fruit fly cost? Use unit analysis and assume all conversions are exact.
18. Light travels 9.46 x 1015 m in
one year. This distance is called a light-year. Calculate the speed of light in metres per second. Use unit
analysis.
19. The following trade ratios are used in a
small country in the Middle East near Iran called
Yrtsimehc. A young man is in love with a
beautiful woman, however, he must
pay a dowry of 12 camels to marry her.
The young man is a yam farmer and has
only 12,000 yams to trade. Can he marry
his true love? Use unit analysis to support your answer.
15 pigs = 2 cows 3 cows = 2 horses 17 chickens = 1 pig
2 horses = 3 camels 20 lbs of figs = 16 chickens
6 yams = 10 lbs of figs
Worksheet # 9 Unit Analysis and Measurement Review
|
Given: |
$0.2045 Can. |
= |
1.00 Francs (French) |
|
|
$2.1860 Can. |
= |
Ł 1.00 (UK) |
|
|
$1.3572 Can. |
= |
$ 1.00 U.S. |
|
|
$0.1534 Can. |
= |
1.00 Peso (Mexico) |
|
|
$0.0109 Can. |
= |
Ą 1.00 (Japanese Yen) |
|
|
$0.0263 Can. |
= |
1.00 Rupee (India) |
|
|
$1.00 U.S. |
= |
1.9325 Marks (Germany) |
Assume all of
the conversions have the number of significant figures indicated.
Convert:
1. $300.00 Can. to Ł.
2. $1025.00 Can. to
pesos.
3. $450.00 U.S. to
yen.
4. Ł 652.23 to
francs.
5. 85.2 Marks to Ł.
6. 3842.35 Yen to
Rupees.
7. 9668.75 Francs to
Marks
Black Market Trading Conversions
Given: 1 Ticket = 2 CDs
5 Buttons = 3
T Shirts
4 Tickets = 1
Back Stage Pass
1 CD = 3 T
Shirts
7 Posters = 3
Buttons
Convert:
1. 28 Posters to buttons.
2. 10. CDs to tickets.
3. 100. Buttons converted to CDs.
4. 1 Back Stage Pass converted to T Shirts.
5. 280. Posters to Back Stage Passes.
6. 6 Back Stage Passes to buttons.
7. 6.372 hL to mL
8. 4.9 x 1015 µg to Mg
9. 8.774 x 103 cm3 to m3
10.
Given the following relationships,
determine how many zings can be obtained when
you trade 20.6 balls.
4 clangs = 3 dangs 7 dangs
= 3 jars 2 balls = 5 clangs
6 jars = 1 zing
11. State the number of significant digits for
each number:
a)
25.0 g b) 1000 g = 1 kg
c)
25.036 A d)
5.214 x 10-62 mL
e) 0.0000005 L f) 8.2000 m
Determine the average and uncertainty
given the following measurements from a
12. Centigram
balance
82.62
g
82.54
g
82.48
g
82.72
g
82.65
g
13.
Show the interval on the number line
that represents the range for the above measurement
after it has been round off correctly.
![]()
Write chemical
formulas for each ionic or molecular compound.
14. Iron III oxide
15. Triphosphorous hexoxide
16. Aluminum hydroxide
17. Nickel II phosphate octahydrate
Name each
chemical formula
11. K3PO4
12. Mn3P2
13. Ga2(SO3)2 . 6H2O
14. P4O10
Worksheet #
10 Unit
1 Practice Test
Balance each
equation.
1. ___Sb + ___Cl2 ® ___SbCl5
2. ___NH3 + ___O2 ® ___N2O5 + ___H2O
3. ___C12H26 + ___O2 ® ___CO2 + ___H2O
4. ___Al
+ ____H2SO4 ® ____H2 + ____Al2(SO4)3
(The next one is the tough one!!)
5. ___Cu
+ ____HNO3 ® ____Cu(NO3)2 + ____NO +____H2O
.
6. Barium
phosphate plus sodium sulphate (both in water) yields solid barium sulphate and
aqueous sodium phosphate. Write a balanced
equation with phase symbols
Write
chemical formulas for each ionic or molecular compound.
7. Mercury II sulfide
8. Diphosphorous pentoxide
9. Barium hydroxide
10. Copper II sulphate hexahydrate
Name each
chemical formula
11. Na3PO4
12. Co3P2
13. Al2(CO3)2 . 6H2O
14. Si2I6
15. Determine the average and uncertainty for
the data:
25.56g
25.54g
25.52g
25.53g
25.55g
Answer
16. Determine the average and uncertainty for
the data:
5.216 oC
5.218 oC
5.213 oC
5.214 oC
5.416 oC
Answer
Round off each
measured number to three significant figures.
17. 0.002567
18. 94549
19. 15.00
Add or subtract
the measured quantities.
20. 15.239
+ 5.36
21. 2.6679
- 1.238
22 12.65449 +
0.2493
23. 8.57
x 107 +
5.37894 x 109
Simplify the following rounding to
the correct number of significant figures.
24. 156
x 256 x
21 x 0.0005687
.02569 x 13.235
x 2654 Answer
25. (8.5
x 10 -24)
(5.37894 x 10-25) ( 4.532 x 1015)
(2.059378 x 10 24) (5.3
x 1022) (9.37894
x 10-13)
Answer
Complete
the relationships:
26. Mg = g 27. km = m
28. L = mL 29. g = ng
30. µs = s 31. cg = g
32. pg =
g 33. s = Ts
Use unit
analysis to perform the following conversions:
34. 8.13
kg to cg.
35. 2.3
x 1012 µm to Mm.
36. 1.52
x 104 Mm to mm.
37. 2.13
Mg to cg.
38. 8.88
x 1012 mm to Mm.
39. 8.52
x 10-8 Mm to pm.
Use unit
analysis and the conversion factors to perform the following conversions:
2.210 lb =
1.000 kg 14 lb = 1 stone (defined) 2000 lb = 1 ton (defined)
1.61 km =
1.00 mile 4.54 L = 1.00
gallon 16 oz = 1 lb
(defined)
40. 635 mL to gal
41. 3.8
stone to oz
42. 25.6 m to miles
43. 26 mi/gal to L/km
44. 14.5 L/km to mi/gal
45. Mr. Iannone’s chemistry class is at a
“Periodic Table” party. Everyone at the party is hungry, and they decide as
a group that everyone wants sushi California rolls. No one at the party has any money
though. One bright student remembers that the class has a credit for 15 pizzas
at Boston Pizza. Using the conversion factors below, will Mr. Iannone’s class be
able to buy enough California rolls for their
“Periodic Table” party if there are 28 students at the party?
1 pizza = 2 Wendy’s burgers 100 brussel sprout =
3 pieces of toast
5 pieces of toast = 1 california
roll 30 tacos = 1 bag of
Doritos
4 Wendy’s burger = 7 tacos 6 lime jello cups =
3 bags of Doritos
1 bowl of lime jello = 1000 brussel
sprouts
Read each scale
and estimate the measurement to the correct number of significant figures.
46.
 Answer.
Answer.
47.
 Answer.
Answer.
48.
 Answer.
Answer.
49.
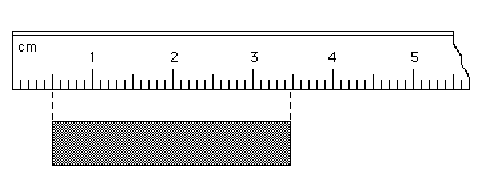
Answer.
50.
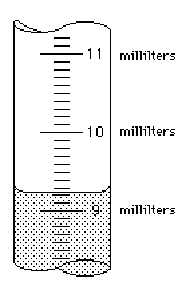 Answer
Answer
51. Micrometer Scale in cm.
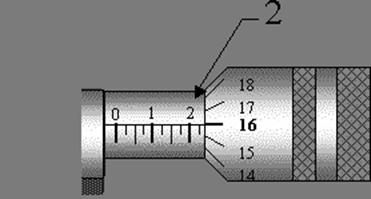
Answer
52. Vernier Scale in cm.
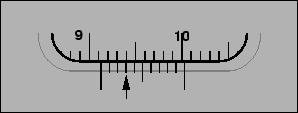 Answer
Answer