1) Which most readily gains electrons?
|
Cu |
Cu+2 |
Fe+2 |
Zn+2 |
Au+3 most readily gains electrons |
2) Which most readily loses electrons?
|
Hg(l) |
Cu+2 |
Sn+4 |
Ba most readily loses electrons |
Al |
Calculate the cell potentials or voltages (E0). Indicate spontaneity.
3. Cl2 + 2Br- -----> 2Cl- + Br2 E0= + 0.27 v spontaneous
4. 2MnO4- + 5Pb + 16H+ -----> 2Mn+2 + 8H2O + 5Pb+2 E0= + 1.64 v spontaneous
5. Will AgNO3 react with Zn? Write a balanced redox reaction and calculate Eo
2Ag+ + Zn ------> 2Ag + Zn+2 E0= + 1.56 v spontaneous Yes!
6. What would happen if you used an iron spoon to stir a soulution of Al2(SO4)3(aq) ? Write a balanced redox reaction and calculate Eo.
3Fe + 2Al+3 ------> 3Fe+2 + 2Al E0= - 1.21 v nonspontaneous No reaction!
7) What are the differences between an electrochemical cell and an electrolytic cell?
|
electrochemical cell |
electrolytic cell |
|
Produces electricity |
Consumes electricity |
|
Spontaneous |
Nonspontaneous |
|
Salt bridge Two beakers |
No salt bridge One beaker |
|
Metal Electrodes |
Inert C or Pt Electrodes |
8) What are the similarities between an electrochemical cell and an electrolytic cell?
|
electrochemical cell or electrolytic cell |
|
The Anode is the site of oxidation and the cathode is the site of reduction. |
|
Anions migrate to the anion and cations migrate to the cathode. |
|
Both have redox reactions. |
|
Electrons flow through a wire from the anode to the cathode |
9) State how you would determine each of the following in an electrochemical or electrolytic cell.
|
|
Electrochemical Cell |
Electrolytic Cell |
|
The site of reduction |
Highest on Reduction Chart |
The Negative Electrode |
|
The site of oxidation |
Lowest on Reduction Chart |
The Positive Electrode |
|
The +ve electrode |
Site of Reduction |
Connected to the power supply +ve |
|
The -ve electrode |
Site of Oxidation |
Connected to the power supply -ve |
|
The anions migrate to the |
Anode |
Anode |
|
The cations migrate to the |
Cathode |
Cathode |
|
The electrode that gains mass |
Cathode |
Neither inert electrodes |
|
The electrode that loses mass |
Anode |
Neither inert electrodes |
|
The electrons flow from |
Anode to Cathode |
Anode to Cathode |
10.a) Draw an operating electrochemical cell using an Al half-cell and a Mg half-cell. Label the parts of the electrochemical cell including the anode or cathode, and all reagents and materials used. Write the reactions and determine the E0.
Cathode Reaction: 2(Al+3 + 3e- ------> Al ) E0= - 1.66
Anode Reaction: 3(Mg -------> Mg+2 + 2e- ) E0= +2.37
Redox Reaction: 2Al+3 + 3Mg -----> 3 Mg+2 + 2 Al E0= +0.71
11. (a) Write the half reaction that occurs at each electrode during the electrolysis of aqueous 1 M NaI.
Anode : 2I- --------> I2 + 2e- E0= -0.54 v
Cathode : 2H2O + 2e- ------> H2 + 2OH- E0= -0.41v
(b) What is the minimum required voltage for this process? E0= +0.95 v
12. (a) Write the half reaction that occurs at each electrode during the electrolysis of molton NaI.
Anode : 2I- --------> I2 + 2e- E0= -0.54 v
Cathode : Na+ + 1e- ------> Na E0= -2.71v
(b) What is the minimum required voltage for this process? E0= +3.25v
13. Aluminum is produced industrially from aluminum oxide, Al2O3. Demonstrate your understanding of this process by
(i) describing how the process is carried out: C electrodes are used in the electrolysis of molten Al2O3.
(ii) writing equations of the reactions involved in the process, and
Anode : 2O-2 --------> O2 + 4e- Cathode : Al+3 + 3e- ------> Al
(iii) describing how the problem of the high melting point of Al2O3 is overcome.
Mixing Al2O3 with cryolyte lowers the melting point from 2000º C to 900ºC, which is suitable for electrolysis.
14. Consider the following redox data:
3V + 2Ga3+ ----> 3V2+ + 2Ga E=+0.64V
3V2+ + 2Al ----> 3V + 2 Al3+ E=+0.46V
Based on these observations, a student concludes that Ga+3 and Al will react spontaneously. List the oxidizing agents in order of decreasing strength. Write reduction reactions for each. Determine the strongest reducing agent. Determine if Ga+3 and Al will react spontaneously.
|
strongest oxidizing agent |
Ga3+ + 3e- ----> Ga |
|
|
|
V2+ + 2e- ----> 3V |
|
|
|
Al3+ + 3e- ----> Al |
strongest reducing agent |
Ga+3 and Al will react spontaneously as Ga+3 is a stronger oxidizing agent than Al+3.
15. Balance the equation for the following half reaction occuring in acid solution:
7 H2O + 2V ----> HV2O7-3 + 13H+ + 10e-
16. Balance the following redox reaction occuring in basic solution:
4 H2O + 2 MnO4- + 3 C2O4-2 -----> 2 MnO2 + 8 OH- + 6 CO2
17. 250ml .200M MnO4- reacts with excess SO3-2. How many grams of MnO2 are produced?
2MnO4- + 3SO3-2 + H2O -----> 2MnO2 + 3SO4-2 + 2OH- 4.35g MnO2
18. Determine the oxidation number for each bold atom.
|
MnO2 |
IO3- |
Cr2O7-2 |
C2O4-2 |
Al(NO3)3 |
NH4Cl |
NaH |
|
+4 |
+5 |
+6 |
+3 |
+3 |
-3 |
-1 |
|
HOOH |
NO3- |
H3PO4 |
Na2C2O4 |
I2 |
N2O3 |
Pt(H2O)4+2 |
|
-1 |
+5 |
+5 |
+3 |
0 |
+3 |
+2 |
19. 250ml of .500M MnO4- are required to titrate a 100ml sample of SO3-2. Calculate the [SO3-2]
2MnO4- + 3SO3-2 + H2O -----> 2MnO2 + 3SO4-2 + 2OH- [SO3-2] = 1.88M
20. How is the breathalyzer reaction used to determine BAC? Write the reaction and describe how it works. BAC is blood alcohol concentration which is related to the concentration of alcohol in the breath. The alcohol in a breath sample reacts with Cr2O7-2 reducing the orange color of the solution.
8 H+ + Cr2O7-2 (orange) + 3C2H5OH ------> 2Cr+3 (green) + 3C2H4O + 7H2O
21. 2H+ + Mg-----> Mg+2 +H2
Determine the Oxidizing agent H+ and the Reducing agent Mg
22. Choose a suitable redox reactant to oxidize Cl- to ClO4- in a redox titration. MnO4- in acid
23. Describe as an electrochemical or electrolytic cell:
|
a) Fuel cell |
electrochemical |
|
b) Charging a car battery |
electrolytic |
|
c) Discharging a car battery |
electrochemical |
|
d) Ni plating |
electrolytic |
|
e) Industrial Al production |
electrolytic |
|
f) Cl2 production |
electrolytic |
|
g) Electrowinning |
electrolytic |
24) Which of the reactants is gaining electrons? Which of the reactants is the oxidizing agent?
Br2 (oxidizing agent and is gaining electrons) + SO2 +Na2SO4 +H2O --------> 2H2SO4 + 2NaBr
25) A student studied the following reactions and she recorded:
Pd+2 + Cu -------> Pd + Cu+2 spontaneous
Pd+2 + Au -------> no reaction
Pd+2 + Hg -------> no reaction
Au+3 + Hg -------> Au + Hg+2 spontaneous
List the oxidizing agents from strongest to weakest. List the reducing agents from strongest to weakest. Predict if the reaction will occur.
|
Strongest Oxidizing agent |
Au+3 + 3e- -------> Au |
|
|
|
Hg+2 + 2e- -------> Hg |
|
|
|
Pd+2 + 2e- -------> Pd |
|
|
|
Cu+2 + 2e- -------> Cu |
Weakest Reducing Agent |
Au+3 + Cu ------------> Yes Spontaneous Reaction
26) Match each type of electrolytic cell with the example cell.
|
Electrowinning |
Pure Al is reduced at the cathode from molten bauxite (Al2O3). |
|
Electroplating |
A silver anode oxidizes & Ag reduces on a Cu cathode |
|
Electrorefining |
Pure Pb is reduced at the cathode while impure Pb oxidizes at the anode |
27.
List the anode, cathode, anode reaction , cathode reaction, and electrolyte for
each commercial electrochemical cell.
|
Cell |
anode |
anode reaction |
cathode |
cathode reaction |
electrolyte |
|
Leclanche or Common Dry Cell |
Zn |
Zn-->Zn+2 + 2e- |
C/MnO2 |
Mn+4 +1e- -----> Mn+3 |
NH4Cl |
|
Alkaline Cell |
Zn |
Zn-->Zn+2 + 2e- |
C/MnO2 |
Mn+4 +1e- -----> Mn+3 |
KOH |
|
Lead Storage or Car Battery |
Pb |
Pb ---> Pb+2+ 2e- |
PbO2 |
PbO2 + SO4-2 + 4OH-1 + 2e- -----> PbSO4 + 2H2O |
H2SO4 |
|
Fuel Cell |
C |
H2 + 2OH- ---> 2H2O + 2e- |
C |
O2 + 2H2O +4e-----> 4OH- |
KOH |
28. Which of the above cells requires continuous input of O2 and H2 and is produced by Ballard Industries. Fuel Cell
29. List the anode, cathode, anode reaction , cathode reaction, and electrolyte for each commercial electrolytic cell.
|
Cell |
anode |
anode reaction |
cathode |
cathode reaction |
electrolyte |
|
Electrolysis of Molten Al2O3 |
C |
O-2 ---> O2 + 2e- |
C |
Al+3 + 3e- ---> Al |
Molten Al2O3 |
|
Electrolysis of Aqueous NaCl |
C |
2Cl- ----> Cl2 + 2e- |
C |
2H2O + 2e-----> H2 + 2OH- |
Aqueous NaCl |
|
Silver-plating a Cu spoon |
Ag |
Ag ---> Ag+ + 1e- |
Cu |
Ag+ + 1e- ---> Ag |
AgNO3(aq) |
|
Electrorefining pure Pb from impure Pb |
Impure Pb |
Pb ---> Pb+2 + 2e- |
Pure Pb |
Pb+2 + 2e- ---> Pb |
PbSiF6 |
30. Describe each term:
|
salt bridge |
U-tube filled with salt solution connecting two half cells in a electrochemical cell. Allows ions to migrate. |
|
electrolyte |
A solution that contains ions and conducts electricity. |
|
anode |
Metal electrode that is the site of oxidation. |
|
cathode |
Metal electrode that is the site of reduction. |
|
spontaneous |
Occurs naturally and has a positive Eo. |
|
electronegativity |
The ability to attract electrons. |
|
cation |
Positive ion. |
|
anion |
Negative ion. |
|
electrochemical cell |
Two metals in electrolytes joined by a salt bridge using spontaneous redox reaction to produce an electrical current. |
|
electrolytic cell |
A power supply connected to inert electrodes in an electrolyte which forces nonspontaneous redox reactions to occur. |
|
oxidation number |
The real or apparent charge of an atom if all bonds are assumed to be ionic. |
|
electrolysis |
What occurs in an electrolytic cell. |
|
oxidation |
Loss of electrons. |
|
reduction |
Gain of electrons. |
|
oxidizing agent |
Causes oxidation by undergoing reducing. |
|
reducing agent |
Causes reduction by undergoing oxidation. |
|
electrode |
Strip of C or Metal used in a cell. |
|
corrosion |
The oxidation of a metal often Fe ---> Fe+2 + 2e- |
|
electrowinning |
The reduction of a metal from its ore by electrolysis. |
|
electrorefining |
The purification of a metal by electrolysis. |
|
overpotential effect |
The higher than normal voltage for the oxidation and reduction of water. |
|
fuel cell |
An electrochemical cell that converts H2 and O2 into H2O and electricity. |
31. Define corrosion of a metal, and illustrate your definition with reference to an example, using appropriate equations. Give TWO methods by which corrosion can be prevented and describe how each method works. The two methods must involve different chemical principles.
The corrosion of iron Cathode: Fe ----> Fe+2 + 2e-
Anode: O2 + 2H2O + 4e- ------> 4OH-
1) Painting prevents the reactants: O2 + 2H2O from colliding with the surface of the metal.
2) Galvinizing allows Zn to corrode (anode) instead of Fe (cathode) due to the action of the chemical cell they produce.
32. Explain why you would choose Zn or Cu to cathodically protect iron? Zn because it oxidizes more readily than Fe forcing Fe to be the cathode or site of reduction.
33. A+2 does not react with B, while C+2 reacts with B. Rank the oxidizing agents in decreasing order of strength. Rank the reducing agents in decreasing order of strength. Will A+2 react with C?
C+2 + 2e- --------> C Oxidizing agents: C+2 B+2 A+2
B+2 + 2e- --------> B Reducing Agents: A B C
A+2 + 2e- --------> A
A+2 will not react with C.
34. Write half reactions for each using the reduction table and list the half cell potential.
|
|
Half Reaction |
Eo |
|
oxidation of water |
H2O --------> 1/2 O2 + 2H+ + 2e- |
-0.82v |
|
oxidation of water in acid |
2 H2O --------> 1/2O2 + 2H+ + 2e- |
-1.23v |
|
reduction of water |
2 H2O + 2e- ------------> H2 + 2OH- |
-0.41v |
|
reduction of water in alkaline |
2 H2O + 2e- ------------> H2 + 2OH- |
-0.83v |
|
oxidation of H2 in water |
H2 + 2OH- ------------> 2 H2O + 2e- |
+0.41 |
|
oxidation of H2 in acid |
H2 ------------> 2H+ + 2e- |
0.00v |
|
oxidation of H2 in base |
H2 + 2OH- ------------> 2 H2O + 2e- |
+0.83 |
|
reduction of Cr2O7-2 in acid |
Cr2O7-2 + 14 H+ + 6 e- -------> 2Cr3+ + 7 H2O |
+1.23v |
|
reduction of HBr |
2H+ + 2e- ------------> H2 |
0.00v |
35.Completely analyze the following electrochemical cell.
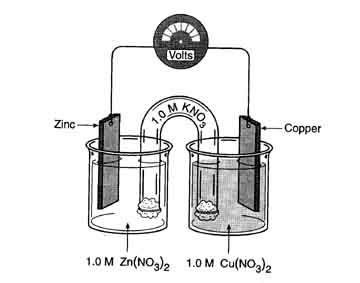
|
The anode reaction is: |
Zn -----------> Zn+2 + 2e- |
|
The cathode reaction is: |
Cu+2 + 2e- -------> Cu |
|
The electrons flow from ___ to ___ |
anode to cathode |
|
The ions that migrate to the Zn electrode are: |
NO3- |
|
The ions that migrate to the Cu electrode are: |
Zn+2 Cu+2 K+ |
|
The intial voltage of this cell is: |
1.10v |
|
The voltage of this cell once equilibrium is reached is: |
0.00v |
|
Describe the change in [Cu+2] in the Cu half cell |
decreases |
|
Describe the change in [NO3-1] in the Zn half cell |
increase |
36. Completely analyze the following electrochemical cell.
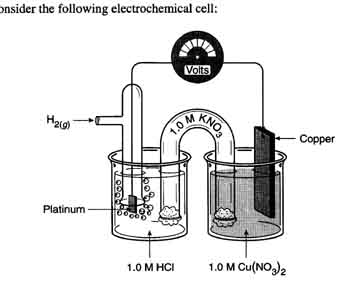
|
The anode reaction is: |
H2 ------------> 2H+ + 2e- |
|
The cathode reaction is: |
Cu+2 + 2e- -------> Cu |
|
The electrons flow from ___ to ___ |
anode to cathode |
|
The ions that migrate to the Pt electrode are: |
NO3- Cl- |
|
The ions that migrate to the Cu electrode are: |
Cu+2 K+ H+ |
|
The intial voltage of this cell is: |
0.34v |
|
The voltage of this cell once equilibrium is reached is: |
0.00v |
|
Describe the change in [Cu+2] in the Cu half cell |
decreases |
|
Describe the change in [NO3-1] in the H+/H2 half cell |
increases |
38. Completely analyze the following electrolytic cell. Note that the electrodes are not inert and because of that, the anode might oxidize.
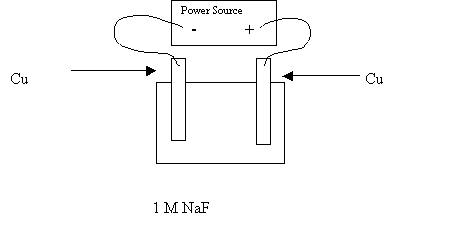
|
Anode Reaction |
Cu ® Cu2+ + 2e- E0 = -0.34 v |
|
Cathode Reaction |
2H2O + 2e- ® H2 + 2OH- E0 = -0.41 v |
|
Chemicals produced at the anode |
Cu2+ |
|
Chemicals produced at the cathode |
H2 OH- |
|
The electrons flow from |
Anode (right) to cathode
(left) |
|
The MTV |
+0.75 v |
|
Which electrode is the anode ? |
right |
38. Completely analyze the following electrolytic cell.
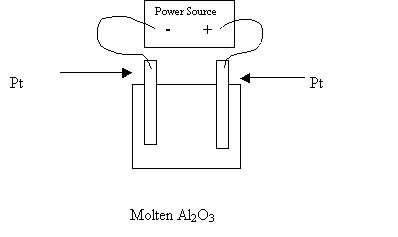
|
Anode Reaction |
2O-2 ---------> O2 +4e- |
|
Cathode Reaction |
Al+3 + 3e- ---------> Al |
|
Chemicals produced at the anode |
O2 |
|
Chemicals produced at the cathode |
Al |
|
The electrons flow from __to __ |
anode to cathode |
|
The chemical used to lower the mp is: |
cryolite |
|
Which electrode is the anode ? |
the one on the right |