Acids Quiz
#9 Titrations and Titration Curves
1. Which of the following indicators would be used when titrating a weak acid with a strong base?
A. Methyl red
B. Methyl violet
C. Indigo carmine
D. Phenolphthalein
2. Which of the following acid-base pairs would result in an equivalence point with pH greater than 7.0?
A. HCl and LiOH
B. HNO3 and NH3
C. HClO4 and NaOH
D. CH3COOH
and KOH
3. Which of the following standardized solutions should a chemist select when titrating a 25.00 mL sample of 0.1 M NH3, using methyl red as an indicator?
A. 0.114
M HCL
B. 6.00 M HNO3
C. 0.105 M NaOH
D. 0.100 M CH3COOH
4. Consider the following 0.100 M solutions
I. H2SO4 II. HCl III. HF
The equivalence point is reached when 10.00 mL of 0.100 NaOH has been added to 10.00 mL of solution(s)
A. II only
B. I and II only
C. II
and III only
D. I, II and III
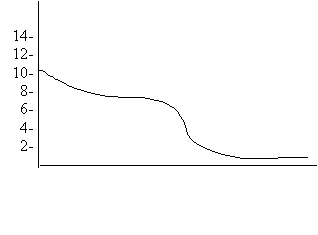 5.
5.
Which pair of 0.10 M solutions would result in the above titration curve?
A. HF and KOH
B. HCl
and NH3
C. H2S and NaOH
D. HNO3 and KOH
6. A suitable indicator for the above titration is
A. Methyl violet
B. Alizarin yellow
C. Thymolphthalein
D. Bromcresol green
7. The pH scale is
A. direct
B. inverse
C. logarithmic
D. exponential
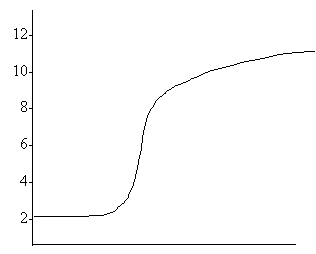 8.
8.
Which of the following indicators should be used in the titration represented by the above titration curve?
A. Orange IV
B. Methyl
red
C. Phenolphthalein
D. Alizarin yellow
9. Which of the following indicators should be used when 1.0 M HNO2 is titrated with NaOH(aq)?
A. Methyl red
B. Thymol
blue
C. Methyl orange
D. Indigo carmine
10. Which of the following solutions should be used when titrating a 25.00 mL sample of CH3COOH that is approximately 0.1 M?
A. 0.150 M NaOH
B. 0.001 M NaOH
C. 3.00 M NaOH
D. 6.00 M NaOH
11. What volume of 0.250 M H2SO4 is required to neutralize 25.00 mL of 2.50 M KOH?
A. 125
mL
B. 150 mL
C. 250 mL
D. 500mL
12. Which of the following pairs of substances form a buffer system for human blood?
A. HCl and Cl-
B. NH3 and NH2-
C. H2CO3
and HCO3-
D. H2C6H5O7
and HC6H5O72-
13. What term is used to describe the point at which a chemical indicator changes
colour?
A. titration point
B. transition point
C. equivalence point
D. indicator point
14. What term is used to describe the point at which a the moles H+ equal the moles
A. titration point
B. transition point
C. equivalence point
D. indicator point
15. Which of the following equations describes the predominant reaction that occurs
at the equivalence point of a titration between CH3COOH(aq) and NaOH(aq)?
A. H+(aq)
+
B. CH3COO-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ CH3COOH(aq) +
C. CH3COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) ® NaCH3COO(aq) + H2O(l)
D. CH3COO-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ CH2COO2-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
16. A salt forms in the reaction between HF(aq) and NaOH(aq). What is the net ionic
equation for the hydrolysis of this salt?
A. NaF(aq) ® Na+(aq) + F-(aq)
B. HF(aq) + H2O(l) ® H3O+(aq) + F-(aq)
C. F-(aq) + H2O(l) ® HF(aq) +
D. F-(aq) + H2O(l) ® H2F+(aq) + O2-(aq)
17. What is the pH in 0.10 M HCN ?
A. 7.0 x 10-6
B. 2.2 x 10-5
C. 4.65
D. 5.15
18. What volume of 0.250 M KOH is required to titrate 0.0200 mol of the weak acid
H2C2O4 ?
A. 80.0 mL
B. 40.0 mL
C. 20.0 mL
D. 10.0 mL
19. What is the approximate pH at the equivalence point when a weak acid is
titrated with a strong base?
A. pH = 9
B. pH = 5
C. pH = 7
D. pH = 14
20. What is the approximate pH at the equivalence point when a strong acid is
titrated with a weak base?
A. pH = 9
B. pH = 5
C. pH = 7
D. pH = 14
21. What term describes the chemical that is used to detect the end point of an acid-
base titration?
A. buffer
B. standard
C. indicator
D. primary standard
22. What term describes a solution of acid or base that can be prepared form a solid
an its concentration can be accurately calculated from the mass of the solid and
the volume of the volumetric flask.
A. buffer
B. standard
C. indicator
D. primary standard
23. Which of the titrations results in pH=7.0 at the equivalence point?
A. A weak acid is titrated with a weak base.
B. A weak acid is titrated with a strong base.
C. A strong acid is titrated with a weak base.
D. A strong acid is titrated with a strong base.
24. What is the pH of a solution prepared by adding 0.50 mol KOH to 1.0 L of
0.30 M HNO3?
A. 0.20
B. 0.70
C. 13.30
D. 13.80
25. A salt forms in the reaction between HF(aq) and NaOH(aq). What is the net ionic
equation for the hydrolysis of this salt?
A. NaF(aq) ® Na+(aq) + F-(aq)
B. HF(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + F-(aq)
C. F-(aq) + H2O(aq) ⇌ HF(aq) +
D. HF(aq) + NaOH(aq) ® NaF(aq) + H2O(l)
26. What is the Ka for the indicator that is yellow in its basic form and blue in its acid
form?
A. 6 x 10-13
B. 2 x 10-9
C. 2 x 10-7
D. 3 x 10-5
27. The pH of an aqueous
solution is 4.32. The [
A. 6.4 x 10-1 M
B. 4.8 x 10-5 M
C. 2.1
x 10-10 M
D. 1.6 x 10-14 M
28. The pH of an
aqueous solution is 10.32. The [
A. 5.0 x 10-12 M
B. 2.0 x 10-11 M
C. 4.8 x 10-11 M
D. 2.1
x 10-4 M
29. The net ionic equation for the hydrolysis of the salt, Na2S is
A. Na2S ⇄ 2Na+ + S2-
B. S2-
+ H2O ⇄
C. Na2S + 2H2O ⇄ 2NaOH + H2S
D. 2Na+ + S2- + 2H2O ⇄ 2Na+ + 2OH- + H2S
30. Consider the following salts:
Which of these salts, when dissolved in water, would form a basic solution?
A. I
only
B. I and II only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III