 |
Quiz # 3 Yield/Graphing Le Chatelier’s Principle
1. When a catalyst is added to an equilibrium system, the forward reaction
A. Increases and the reverse decreases
B. Decreases and the reverse decreases
C. Decreases and the reverse increases
D.
Increases and the reverse increases
2. Consider the following concentration versus time graph for the equilibrium
N2O4(g) ⇄ 2NO2(g)

“t” TIME(S)
At time= “t”, which one of the following stresses occurred
A. Catalyst was added
B. Pressure was changed
C. Temperature was changed
D. Concentration of NO2 was changed
3. Which of the following reactions will shift left when pressure is increased and when temperature is decreased?
A. N2(g) + 2O2(g) + heat ⇄ 2NO2(g)
B. N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) + heat
C.
CH4(g) +
H2O(g) +
heat ⇄ CO(g) + 3H2(g)
D. CS2(g) + 4H2(g) ⇄ CH4(g) + 2H2S(g) + heat
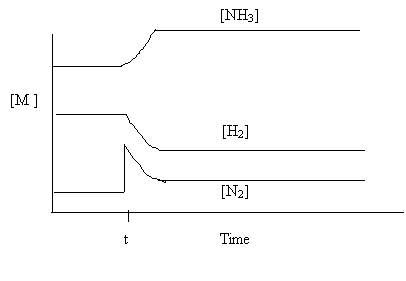
4. Consider the following graph, which relates to this equilibrium
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) ∆H = -92kJ
Which of the following caused the changes in the concentrations at time t ?
A. Addition
of N2
B. Removal of H2
C. Decrease in temperature
D. Decrease in reaction volume
5. Consider the following equilibrium: CH4(g) + H2O(g) + heat ⇄ CO(g) + 3H2(g)
In which of the following will both stresses shift the equilibrium right
A. A decrease in temperature and a decrease in volume
B. An increase in temperature and a decrease in volume
C. A decrease in temperature and an increase in volume
D. An increase in temperature and an increase in volume
6. Consider the following equilibrium system: N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) + 92 kJ
In order to maximize the yield for this reaction, the best conditions are:
A. Low pressure and low temperature
B. Low pressure and high temperature
C. High temperature and low pressure
D. High pressure and low temperature
7. Consider the following equilibrium system: NH3(aq)
+ H2O(l) ⇄ NH+4(aq)
+
Which of the following when added to the above equilibrium system would cause an increase in [OH-]
A. NH3
B. H2O
C. NH4+
D. HCl
8. Consider the
following reversible reaction: Fe3+(aq) +
SCN-(aq) ⇄ FeSCN2+(aq)
A solution of Fe(NO3)3 is added to a solution of KSCN. Which one of the following statements
describes the changes in forward and reverse reaction rates as the reaction moves towards equilibrium?
A. Forward and reverse rates increase
B. Forward and reverse rates decrease
C. Forward rate increases and reverse rate decrease
D.
Forward rate decreases and reverse
rate increase
9. Consider the following equilibrium: N2(g) + O2(g) ⇄ 2NO(g) ∆H= + 181 kJ
When the temperature is decreased, the equilibrium
A.
Shifts left and [NO] decreases
B. Shifts left and [NO] increases
C. Shifts right and [NO] increases
D. Shifts right and [NO] decreases
10. Consider the following equilibrium: N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) + 92 kJ
In which of the following will both changes shift the equilibrium right?
A. An increase in volume and a decrease in temperature
B. An increase in volume and a increase in temperature
C.
A decrease in volume and a decrease in temperature
D. A decrease in volume and an increase in temperature
11. Consider the following equilibrium: CaCO3(s) + 556 kJ ⇄ CaCO(s) + CO2(g)
The equilibrium will shift to the right
A. CO2 is added
B. CaCO3(s) is added
C.
The temperature is increased
D. The temperature is decreased
12. Consider the following equilibrium: SO2(g) + NO2(g) ⇄ SO3(g) + NO(g) + energy
The equilibrium does not shift with a change in the
A. Volume
B. Temperature
C. Concentration of products
D. Concentration of reactants
13. Consider the following equilibrium: 2Hl(g) ⇄ H2(g) + I2(g)
At constant temperature and volume, more I2 is added to the above equilibrium. A new state of equilibrium
results from a shift to the
A. Left with a net decrease in [H2]
B. Left with a net increase in [H2]
C. Right with a net increase in [H2]
D. Right with a net decrease in [H2]
14. Consider the following diagram for the equilibrium system:
Energy + N2O4(g) ⇄ 2NO2(g)
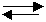
A. [NO2] was increased.
B. [N2O4] was decreased.
C. Temperature was increased.
D. Temperature was decreased.
15. Consider the following diagram for the equilibrium system:
Energy + N2O4(g) ⇄ 2NO2(g)
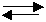
A. [NO2] was increased.
B. [N2O4] was decreased.
C. Temperature was increased.
D. Temperature was decreased.
16. Consider the following diagram for the equilibrium system:
Energy + N2O4(g) ⇄ 2NO2(g)
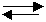
A. [NO2] was increased.
B. [N2O4] was decreased.
C. Temperature was increased.
D. The Volume was decreased.
17. Which of the following describes the temperature and pressure needed for the maximum yield of NO2?
Energy + N2O4(g) ⇄ 2NO2(g)
Temperature Pressure
A. low low
B. low high
C. high low
D. high high
18. Which of the following describes the temperature and pressure needed for the maximum yield of NH3?
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) + 92 kJ
Temperature Pressure
A. low low
B. low high
C. high low
D. high high
19. Which of the following describes the temperature and pressure needed for the maximum yield of CO2?
CaCO3(s) ⇄ CaCO(s) + CO2(g) ΔH = +215 kJ
Temperature Pressure
A. low low
B. low high
C. high low
D. high high
20. Consider the following equilibrium: CaCO3(s) ⇌ CaO(s) + CO2(g) ΔH = +160 kJ
Which starting materials could establish an equilibrium?
1 CaCO3(s) 2 CaO(s)
3 CaO(s) and CO2(g) 4 CaCO3(s) and CO2(g)
A. 1, 2, 3 only
B. 1, 2, 4 only
C. 1, 3, 4 only
D. 3, 4 only
Consider the following reaction for the next five questions 21 to 25.
4NH3(g) + 3O2(g) ⇌ 2N2(g) + 6H2O(l) + 1250 kJ
21. Which of the following would cause the concentration of NH3 at equilibrium to increase?
A. an increase in [O2]
B. a increase in volume
C. a decrease in temperature
D. an increase in temperature
22. What happens when NH3 is added to the above system?
Equilibrium [N2]
A. no shift unchanged
B. shifts right decreases
C. shifts right increases
D. shifts left increases
23. If some O2 is removed from the system, what happens to the forward and reverse reaction
rates after equilibrium is re-established?
Forward Reaction Rate Reverse Reaction Rate
A. increases decreases
B. decreases decreases
C. increases increases
D. decreases increases
24. If some O2 is injected into the system, what happens to the forward and reverse reaction rates
during the shift to re-establish equilibrium?
Forward Reaction Rate Reverse Reaction Rate
A. increases decreases
B. decreases decreases
C. increases increases
D. decreases increases
25. Consider the
equilibrium: N2(g) +
3H2(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) +
92 kJ
The following diagram represents the rate of the reverse reaction.
t1
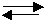
Which of the following stresses explains what happened at t1 ?
A. [H2] increased.
B. [N2] decreased.
C. [NH3] increased.
D. [NH3] decreased.
26. Consider the
equilibrium: N2(g) +
3H2(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) +
92 kJ
The following diagram represents the rate of the forward reaction.
t1
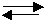
Which of the following stresses explains what happened at t1 ?
A. [H2] increased.
B. temperature was lowered
C. [NH3] increased.
D. [NH3] decreased.
27. Consider the
equilibrium: N2(g) +
3H2(g) ⇄ 2NH3(g) +
92 kJ
The following diagram represents the rate of the reverse reaction.
t1
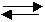
Which of the following stresses explains what happened at t1 ?
A. [H2] increased.
B. [N2] decreased.
C. [NH3] increased.
D. [NH3] decreased.
28. A small amount of NaOH is added to the following equilibrium system:
2CrO42- + 2H+ ⇌ Cr2O72-(aq) + H2O(l)
How do the [CrO42-] and the reverse reaction rate change as equilibrium is re-established?
[CrO42-] Reverse Rate
A. increases increases
B. increases decreases
C. decreases decreases
D. decreases increases
29. A small amount of H2SO4 is added to the following equilibrium system:
2CrO42- + 2H+ ⇌ Cr2O72-(aq) + H2O(l)
How do the [CrO42-] and the reverse reaction rate change as equilibrium is re-established?
[CrO42-] Reverse Rate
A. increases increases
B. increases decreases
C. decreases decreases
D. decreases increases
30. A small amount of NaOH is added to the following equilibrium system:
2CrO42- + 2H+ ⇌ Cr2O72-(aq) + H2O(l)
How do the [Cr2O72-] and the reverse reaction rate change as equilibrium is re-established?
[Cr2O72-] Reverse Rate
A. increases increases
B. increases decreases
C. decreases decreases
D. decreases increases
31. A small amount of H2SO4 is added to the following equilibrium system:
2CrO42- + 2H+ ⇌ Cr2O72-(aq) + H2O(l)
How do the [Cr2O72-] and the reverse reaction rate change as equilibrium is re-established?
[Cr2O72-] Reverse Rate
A. increases increases
B. increases decreases
C. decreases decreases
D. decreases increases