Kinetics Quiz 4 Potential Energy Diagrams
1. A catalyst increases the rate of a reaction by
A. Increasing the concentration of the reactant(s)
B. Decreasing the concentration of the reactant(s)
C. Increasing the activation energy of the overall reaction
D. Decreasing the activation energy of the overall reaction
2. Consider the following Reaction: ½ N2(g) + ½ O2(g) → NO(g)
∆H = +90 kJ/mol NO
The correct equation including the heat term is
A. N2(g) + O2(g) +90 kJ
------- > 2NO(g)
B. N2(g) + O2(g) +180 kJ
------- > 2NO(g)
C. N2(g) + O2(g) ------- > 2NO(g) +90kJ
D. N2(g) + O2(g) ------- > 2NO(g) +180kJ
3. A forward reaction has an activation energy of 50 kJ and a ∆H of –100 kJ.
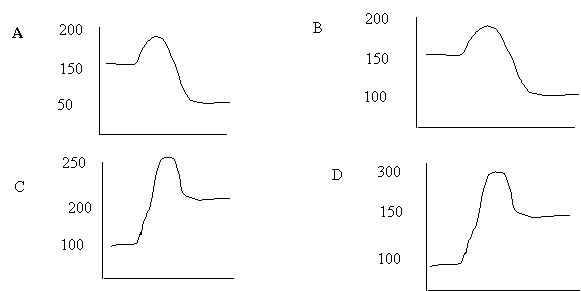 The
PE diagram, which describes this reaction, is
The
PE diagram, which describes this reaction, is
4. Consider the following potential energy
diagram 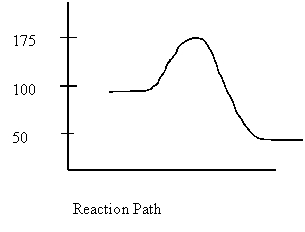
The Activation energy for the forward reaction is
A. 25 kJ
B. 50 kJ
C. 75 kJ
D. 125 kJ
5. Consider the
following reaction: ½ H2(g) +
½ I2(g) ------- >
HI(g)
The activation energy for the formation of HI is 167 kJ and for the decomposition of HI is 139 kJ. The reaction for the formation of HI is
A. Exothermic and the ∆H = -28 kJ
B. Exothermic and the ∆H = +28 kJ
C. Endothermic and the ∆H = -28 kJ
D. Endothermic and the ∆H = +28 kJ
6. Consider the following potential energy diagram
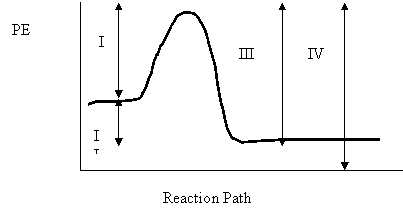
The energy interval the represents the activation energy for the reverse reaction is
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
7. As reactant molecules approach each other
A. Heat is released
B. A reaction intermediate forms
C. Kinetic energy changes to potential energy
D. Potential energy changes to kinetic
8. Which of the following equations represents an endothermic reaction?
A. N204(g) +
59 kJ ------- > 2NO2(g)
B. 2H2(g) + 02(g) ------- > 2H2O(l) + 572 kJ
C. 2BrCl(g) – 29.3 kJ ------ > Br2(g) + Cl2(g)
D. C(s) + O2(g) ------- > CO2(g) ∆H = -394 kJ
9. Consider the following potential energy diagram
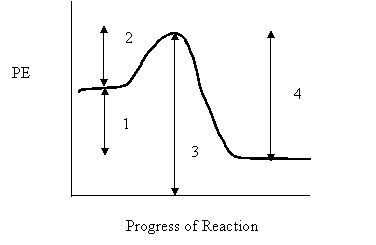
The interval representing ∆H for the reverse reaction is
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
10. Which of the following corresponds to the fastest reaction at room temperature
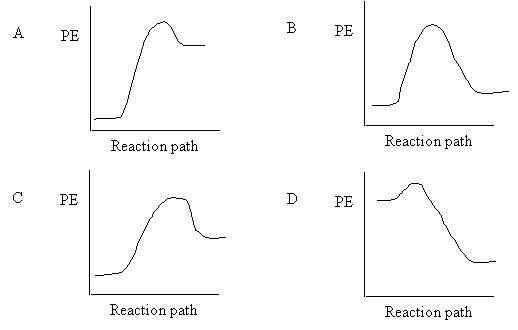
|
|
|
|
|
|
11. When a catalyst is added to a reaction, ∆H will
A. Increase slowly
B. Remain constant
C. Decrease slowly
D. Increase rapidly due to alternate pathway
12. Consider the following potential energy diagram that represents two different reactions. Which of the following statements is correct?
 A B
A B
A. Reactions A and B are both exothermic
B. Reactions A and B are both endothermic
C. Reaction A is exothermic and reaction B is endothermic
D. Reaction A in endothermic and reaction B is exothermic
13. Consider the following reaction: ½ H2(g) + ½ I2(g) ------- > HI(g) ∆H = +28 kJ
The activation energy for the formation of HI is 167 kJ. the activation energy for the decomposition of HI is:
A. 28 kJ
B. 139 kJ
C. 167 kJ
D. 195
kJ
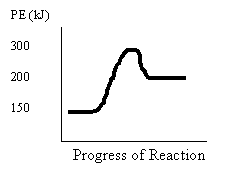 14.
Consider the following potential
energy diagram for 14 to 16
14.
Consider the following potential
energy diagram for 14 to 16
Which of the following are the values for the activation energy Ea and change in enthalpy ΔH for the forward reaction?
Ea(kJ) ΔH(kJ)
A. 300 –50
B. 150 +50
C. 100 –50
D. 100 +50
15. Which of the following are the values for the activation energy Ea and change in enthalpy ΔH for the reverse reaction?
Ea (kJ) ΔH (kJ)
A. 300 –50
B. 150 +50
C. 100 –50
D. 100 +50
16. What is the PE of the reactants and activated complex?
Reactants (kJ) Activated Complex (kJ)
A. 50 50
B. 300 150
C. 200 200
D. 150 300
17. Which of the following would have a positive value for ΔH?
II. the burning of a candle
III. an explosive
reaction
IV. a chemical cold pack
A. III only
B. IV only
C. I and IV
D. II and III
18. Which of the following represents the value for the activation energy of the forward reaction in an equilibrium system?
A. Ea forward = Ea reverse + ΔH
B. Ea forward = Ea reverse - ΔH
C. Ea forward = ΔH - Ea reverse
D. Ea forward = ΔH - Ea forward
19. Consider the following reaction: H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
As a molecule of H2 approaches a molecule of Cl2 on a collision course, how do the KE and PE change?
KE PE
A. increases decreases
B. decreases increases
C. decreases decreases
D. increases increases
20. Consider the following reaction: H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
As the activated complex forms changes to HCl
KE PE
A. increases decreases
B. decreases increases
C. decreases decreases
D. increases increases
21. The activated complex is best described as:
A. stable maximum PE minimum KE
B. stable minimum PE maximum KE
C. unstable maximum PE minimum KE
D. unstable minimum PE maximum KE
22. In a certain reaction ΔH = -136 kJ and Ea reverse = 236 kJ. Which of the following is true of its forward reaction?
A. The reaction is exothermic and Ea = -100 kJ.
B. The
reaction is exothermic and Ea = 100 kJ.
C. The reaction is endothermic and Ea = 372 kJ.
D. The reaction is endothermic and Ea = 232 kJ
23. In a certain reaction ΔH = -136 kJ and Ea = 96 kJ. Which of the following is true about the reverse reaction?
A. The reverse reaction is exothermic and Ea = -40 kJ.
B. The reverse reaction is exothermic and Ea = 40 kJ.
C. The reverse reaction is endothermic and Ea = 96 kJ.
D. The reverse reaction is endothermic and Ea = 232kJ
24. Consider the following information for a reversible chemical reaction:
Forward activation energy 20 kJ Reverse activation energy 30 kJ
Which of the following describes the reaction type and enthalpy change for the forward reaction?
Reaction Type ΔH Value
A. exothermic 10 kJ
B. exothermic -10 kJ
C. endothermic 10 kJ
D. endothermic -10 kJ
25. Consider the following information for a reversible chemical reaction:
Forward activation energy 20 kJ Reverse activation energy 30 kJ
Which of the following describes the reaction type and enthalpy change for the reverse reaction?
Reaction Type ΔH Value
A. exothermic 10 kJ
B. exothermic -10 kJ
C. endothermic 10 kJ
D. endothermic -10 kJ
26.
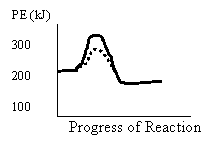
Which of the following is true for the forward reaction?
Reaction PE of Activated Complex (kJ) ΔH (kJ)
A. catalyzed 100 -50
B. uncatalyzed 300 -50
C. catalyzed 250 +50
D. uncatalyzed 150 -50
27. An activated complex can be described as
A. a particle of maximum KE and minimum PE.
B. a stable particle found in a reaction mechanism.
C. an unstable particle that is neither reactant nor product.
D. a particle which is first used then regenerated in a reaction mechanism.
28. Which of the following describes the Ea of a fast reaction and the stability of its activated complex?
Ea Activated Complex
A. small unstable
B. small stable
C. large unstable
D. large stable
29. As an activated complex changes into products, what changes occur in the chemical bonds of the activated complex and the PE of the system?
Bonds PE
A. form increases
B. form decreases
C. break increases
D. break decreases
30. As reactants change into an activated complex, what changes occur in the chemical bonds of the activated complex and the PE of the system?
Bonds PE
A. form increases
B. form decreases
C. break increases
D. break decreases
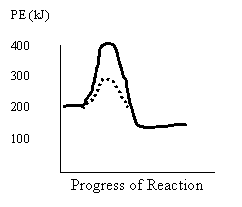 Use
this diagram for 30 -32
Use
this diagram for 30 -32
31. Which of the following describes the reverse reaction?
Activation Energy (kJ) ∆H (kJ)
A. uncatalyzed 200 −100
B. catalyzed 200 −100
C. uncatalyzed 300 +100
D. catalyzed 300 +100
32. Consider the following reaction:
CH4 + Cl2 → CH2Cl2 + H2
Which answer best describes the activated complex?
Formula KE relative to reactants
A. CH4 higher
B. CH4 lower
C. CH4Cl2 higher
D. CH4Cl2 lower