Redox Practice Test 2 Answers
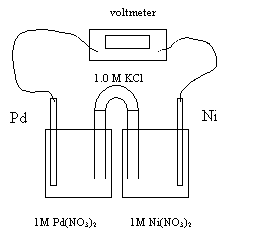
1. As the cell operates, the electrons flow from the nickel electrode to the palladium electrode. The reaction occurring at the anode is
A Pd → Pd2+ + 2e-
B Ni →
Ni2+ + 2e-
C Pd2+ + 2e- → Pb
D Ni2+ + 2e- → Ni
2. As the cell operates,
A both the K+ and the NO3- migrate into the nickel half-cell
B both the K+ and the NO3- migrate into the palladium half-cell
C the K+ migrates into the nickel half-cell and the NO3- migrates into the palladium half-cell
D the K+
migrates into the palladium half-cell and the NO3- migrates
into the nickel half-cell
3. The initial cell voltage is 1.21 V. The reduction potential of Pd2+ is
A -1.21 V
B -.95 V
C +0.95
D +1.21 V
4. What substances are formed at the anode and cathode during electrolysis of molten sodium chloride, NaCl(l)?
Anode Cathode
A O2 H2
B Na Cl2
C Cl2 H2
D Cl2 Na
5. Consider the following electrolytic cell:
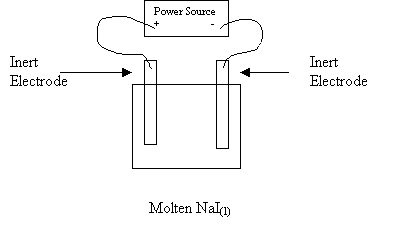
In the cell above
A I- migrates to the anode and gains electrons
B I- migrates to the cathode and loses electrons
C Na+ migrates to the anode and loses electrons
D Na+
migrates to the cathode and gains electrons
6. Which of the following are necessary for electroplating to occur using an electrolytic cell?
I Two electrodes
II A metal being reduced
III A direct current power supply
A I and II only
B I and III only
C II and III only
D I, II, and
III
7. A fuel cell consumes H2 and O2 gas, uses a KOH electrolyte, and produces electricity. The reaction at the anode is
A 2H+ + 2e- → H2
B 1/2O2 + 2H+ + 2e- → H2O
C 4OH- → O2 + 2H2O + 4e-
D H2 +
2OH- → 2H2O + 2e-
8. A student investigating redox reactions recorded the following results:
V2+ + Te2- → no reaction
U4+ + Te2- → U3+ + Te
Based on these results, the strengths of the oxidizing agents, arranged from strongest to weakest, are
A V2+ Te U4+
B U4+ Te V2+
C U3+ Te2- V2+
D V2+ Te2- U3+
9. What is the minimum voltage required to form nickel from an aqueous solution of NiI2 using inert electrodes?
A 0.26 V
B 0.28 V
C 0.54 V
D 0.80 V
10.
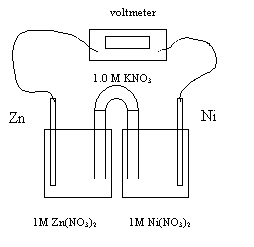
Which of the following occurs as the cell operates?
A the Zn electrode is reduced and increases in mass
B the Zn electrode is reduced and decreases in mass
C the Zn electrode is oxidized and increases in mass
D the Zn
electrode is oxidized and decreases in mass
11. Which of the following reactants would produce an E0 of +0.63 V?
A Ag+ + I2
B Pb2+ +
Zn
C Mg2+ + Ca
D Zn2+ + Mn
12. The concentration of Fe2+(aq) can be determined by a redox titration using
A KBr
B SnCl2
C KMnO4 (basic)
D KBrO3
(acidic)
13. Which of the following will oxidize Fe2+?
A I2(s)
B Ni(s)
C Zn(s)
D Br2(l)
14. The oxidation number of carbon in C2O42- is
A +3
B +4
C +5
D +6
15. Consider the following reaction: 3As2O3 + 4NO3- + 7H2O → 6H3AsO4 + 4NO
The oxidizing agent is
A H+
B H2O
C NO3-
D AsO3
16. When W2O5 is converted to WO2 in a redox reaction, the W has been
A reduced since its oxidation number has increased
B reduced
since its oxidation number has decreased
C oxidized since its oxidation number has increased
D oxidized since its oxidation number has decreased
17. Consider the following:
I Water
II Oxygen gas
III Nitrogen
At 25oC, a piece of iron rusts in the presence of
A I only
B III only
C I and II
only
D II and III only
18. Which of the following represents a redox reaction?
A H2CO3 → H2O + CO2
B CuS +
H2 → H2S + Cu
C AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3
D 2HCl + Na2SO3 → 2NaCl
19. The following reaction occurs in an electrochemical cell: 3Cu2+ + Cr → 2Cr3+ + 3Cu
The Eo for the cell is
A 0.40 V
B 0.75 V
C 1.08 V
D 2.50 V
20. During the corrosion of magnesium, the anode reaction is
A Mg →
Mg2+ + 2e-
B Mg2+ + 2e- → Mg
C 4OH- → O2 + 2H2O + 4e-
D O2 + 2H2O + 4e- → 4OH-
21. A molten binary salt, ZnCl2, undergoes electrolysis. The cathode reaction is
A Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
B 2Cl- → Cl2 + 2e-
C Cl2 + 2e- → 2Cl-
D Zn2+ +
2e- → Zn
22. Which of the following represents a redox reaction?
A CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
B SiCl4 +
2Mg → Si
+ 2MgCl2
C 2NaOH + H2SO4 → 2H2O + Na2SO4
D AbBr + 2S2O32- → Ag(S2O3)23- + Br-
23. The process of applying an electric current through a cell to produce a chemical change is called
A corrosion
B ionization
C hydrolysis
D electrolysis
24. A student investigating redox reactions recorded the following results:
V2+ + Te2- → no reaction
U4+ + Te2- → U3+ + Te
Based on these results, the strengths of the oxidizing agents, arranged from strongest to weakest, are
A V2+ Te U4+
B U4+ Te V2+
C U3+ Te2- V2+
D V2+ Te2- U3+
25. A spontaneous redox reaction occurs when Sn2+ is mixed with
A I2
B Cu
C H2S
D Ag2S
26. Consider the redox reaction: 2BrO3- + 10Cl- + 12H+ → Br2 + 5Cl2 + 6H2O
the oxidation half-reaction ivolved in this reaction is
A 2Cl- →
Cl2 + 2e-
B 2H+ → H2 + 2e-
C BrO3- + 6H+ + 5e- → ½ Br2 + 3H2O
D BrO3- + 6H+ → ½ Br2 + 3H2O + 5e-
27. Which of the following is not a redox reaction?
A Cu + Br2 → CuBr2
B CO + H2O → CO2 + H2
C CH4 + O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
D NaOH +
HCl → NaCl
+ H2O
28. During the electrolysis of 1.0 M Na2SO4, the reaction at the cathode is
A Na+ + 1e- → Na
B 2SO42- → S2O82- + 2e-
C 2H2O → O2 + H+ + 4e-
D 2H2O + 2e- →
H2 + 2OH-
29. An oxidizing agent will cause which of the following changes?
A PtO2 → PtO
B PtO3 → PtO2
C Pt(OH)2 → Pt
D Pt(OH)22+ →
PtO3
30. Consider the overall reaction of the nickel-cadmium battery:
NiO2(s) + Cd(s) + 2H2O(l) → Ni(OH)2(s) + Cd(OH)2(s)
Which of the following occurs at the anode as the reaction proceeds?
A Cd loses 2e- and forms
Cd(OH)2(s)
B Cd gains 2e- and forms Cd(OH)2(s)
C NiO2 loses 2e- and forms Ni(OH)2(s)
D NiO2 gains 2e- and forms Ni(OH)2(s)
31. Which of the following can be produced by the electrolysis from a 1.0 M aqueous solution containing its ions?
A nickel
B sodium
C aluminum
D magnesium
32. In the electrolysis of molten ZnCl2 using carbon electrodes, the reaction that occurs at the anode is
A Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
B Zn2+ + 2e- → Zn
C 2Cl- →
Cl2 + 2e-
D Cl2 + 2e- → 2Cl-
33. In order for the electrolytic cell to operate, it must have
A a voltmeter
B a salt bridge
C a power supply
D an aqueous solution
Subjective
1. a) Indicate in the blank spaces on the following chart whether or nor a reaction will occur when the metals are added to the aqueous ions.
Pd Rh Pt
Pd2+ Spontaneous Nonspontaneous
Rh2+ no reaction no reaction
Pt2+ reaction reaction
b) List the oxidizing agents in order of strongest to weakest
Pt2+ Pb2+ Rh2+
2. Consider the following reaction for the formation of rust:
Fe(s) + ½ O2(g) + H2O(l) → Fe(OH)2
Describe and explain two methods, using different chemical principles, to prevent the formation of rust.
a) Paint- Prevent
collisions between reactants
b) Cathodic Protection- Attach a piece of Zn and Mg.
3. Consider the following redox reaction:
H2Se + SO42- + 2H+ → Se + H2SO3 + H2O
Calculate the Eo for the reaction.
H2Se →
Se + 2H+ + 2e- +0.40 V
SO42- + 2H+ + 2e- → H2SO3 + H2O +0.17 V
4. Balance the following redox reaction in basic solution:
Au + Cl- + O2 → AuCl4- + OH-
4( Au
+ 4Cl- →
AuCl4- + 3e-)
3( 3H+ + 4e- + O2 →
OH- + H2O)
4Au + 16 Cl- + 9H+ + 3O2 →
4AuCl4-
3OH- + 3H2O
+ 9OH- +9OH-
4Au + 16Cl- 6H2O + 3O2 → 4AuCl4- + 12OH-
5. Draw and label a simple electrolytic cell capable of electroplating and inert electrode with silver.
Power Source
+ -
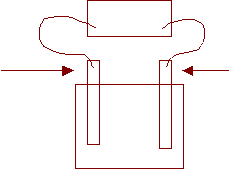
Anode Inert
Cathode
AgNO3(aq)
6. During the production of magnesium metal from sea water, magnesium ions are first precipitated from sea water as magnesium hydroxide.
a) The magnesium hydroxide is neutralized by hydrochloric acid, producing magnesium chloride. Write the neutralization reaction.
Mg(OH)2 +
2HCl → MgCl2 + 2H2O
b) The salt produced, magnesium chloride, is dried melted and undergoes electrolysis. Write the reaction at each electrode.
Anode 2Cl- →
Cl2 + 2e-
Cathode Mg2+ + 2e- →
Mg
c) It is not possible to remove Mg from a 1.0 M solution. Explain why?
Because water would reduce instead of Mg. Water has a higher reduction potential.
7. Consider the following diagram in the electrorefining of lead:
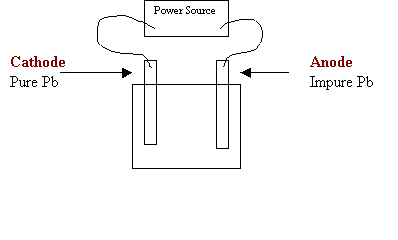
a) On the diagram above, label the anode and cathode.
b) Write the formula for a suitable electrolyte.
Pb(NO3)2 or any soluble compound
containing Pb
c) Write the equation for the reduction half-reaction.
Pb2+ + 2e- → Pb