1.
The following represents the process used to produce iron from iron III oxide:
Fe2O3 +
3CO → 2Fe +
3CO2 What is the
reducing agent in this process?
A. Fe
B. CO
C. CO2
D. Fe2O3
2.
Consider the following reaction: 2HNO2 + 2I- + 2H+ →
2NO + I2 +2H2O
The
oxidation number for each nitrogen atom
A. increases
by 1
B. increases
by 2
C. decreases by 1
D. decreases
by 2
3.
Which of the following reactions is spontaneous?
A. 2I- +
Ag → Ag+ + I2
B. Co2+ +
Cu → Co
+ Cu2+
C. Cu2+ +
Pb → Pb2+ + Cu
D. Ni2+ +
2Ag → 2Ag+ + Ni
4.
Consider the following redox reaction for a lead-acid storage cell:
Pb +
PbO2 + 4H+ + 2SO42- →
2PbSO4 + 2H2O
The
balanced, reduction half reaction is
A. Pb + SO42- →
2PbSO4 + 2e-
B. Pb + 2H+ + SO42- →
PbSO4 + 2H2O + 2e-
C. PbO2 + 4H+ + SO42- + 2e- → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
D. PbO2 +
2SO42
+ 2H2O + 2e- →
PbSO4 + 2OH-
5.
Consider the following reaction: Cd2+(aq) +
Zn(s) → Cd(s)
+ Zn2+(aq)
The
potential for the reaction is +0.36 V. What is the reduction potential for the
cadmium ion?
A. -1.12
V
B. -0.40 V
C. +0.40
V
D. +1.12
V
6.
Which of the following involves a nonspontaneous redox reaction?
A. fuel
cell
B. electroplating
C. redox
titration
D. carbon
dry cell
7.
Consider the following redox reaction:
2MnO4-
+ 16H+ +
5Sn2+ → 2Mn2+ + 8H2O +
5Sn4+
In
a redox titration, 0.60 mole of KMnO4 reacts completely with a
solution of Sn(NO3)2. How many moles of Sn(NO3)2
were present in the solution?
A. 0.024
moles
B. 0.060
moles
C. 1.5 moles
D. 0.30
moles
8.
Which of the following is not a redox reaction?
A. Cu + Br2 →
CuBr2
B. CO + H2O →
CO2 + H2
C. CH4 + H2O →
CO2 + 2H2O
D. NaOH
+ HCl → NaCl + H2O
9.
What is the minimum voltage required to form nickel from an aqueous solution of
NiI2 using inert electrodes?
A. 0.26
V
B. 0.28
V
C. 0.54
V
D. 0.80 V
10.
What substances are formed at the anode and cathode during electrolysis of
molten sodium chloride?
Anode Cathode
A. O2 H2
B. Na Cl2
C. Cl2 H2
D. Cl2 Na
11.
A solution containing an unknown cation reacts spontaneously with both zinc and
copper. The unknown cation is
A. 1.0
M H+
B. 1.0 M Ag+
C. 1.0
M Sr2+
D. 1.0
M Mn2+
12.
Which of the following half-reactions are balanced?
A. ClO- + H2O + e- →
Cl2 + 2OH-
B. 2ClO- + H2O + 2e- →
Cl2 + 3OH-
C. 2ClO- + 2H2O + 2e- →
Cl2 + 4OH-
D. 2ClO- + 2H2O →
Cl2 + 4OH-
+ 2e-
13.
Which of the following is a spontaneous redox reaction?
A. Ag+ + I- →
AgI
B. Ag+ + Fe2+ →
Ag + Fe3+
C. 3Ag+ +
Au → 3Ag
+ Au3+
D. 2Ag+ + Ni2+ →
2Ag + Ni
14.
Salting the roads during the winter increases the amount of corrosion of cars.
The is because the salt
A. reacts
with the iron
B. provides an electrolyte
C. acts
as a reducing agent
D. acts
as an oxidizing agent
Consider
the following electrochemical cell for the next five questions.
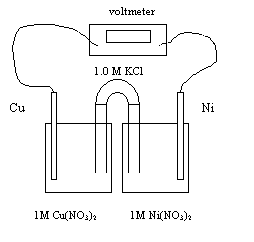
15.
The half-reaction that occurs at the anode is
A. Ni
→ N2+ + 2e-
B. Ni2+ →
2e- + Ni
C. Cu →
Cu2+ + 2e-
D. Cu2+ →
2e- + Cu
16.
The half-reaction that occurs at the cathode is
A. Ni →
N2+ + 2e-
B. Ni2+ + 2e- →
Ni
C. Cu → Cu2+ + 2e-
D. Cu2+ + 2e- →
Cu
17.
The cell potential or Eo is
A. 0.41 V
B. 0.78
V
C. 0.34
V
D. 0.60 V
18.
The following ions migrate to the Cu electrode
A. K+ Cu2+ Ni2+
B. Cu2+ Ni2+
C. Cl- NO3-
D. Cl- NO3- 2e-
19.
The electrons flow
A. through
the salt bridge from Cu to Ni
B. through
the salt bridge from Cu to Ni
C. through
the wire from Cu to Ni
D. through the wire from Ni to Cu
20.
Which of the following will not react spontaneously with 1.0 M HCl?
A. tin
B. lithium
C. mercury
D. magnesium
21.
Which of the following can be produced by electrolysis from a 1.0 M aqueous
solution containing its ion?
A. nickel
B. sodium
C. aluminum
D. magnesium
22.
In order for an electrolytic cell to operate, it must have
A. a
voltmeter.
B. a
salt bridge.
C. a power supply.
D. an
aqueous solution.
23.
In the electrolysis of molten ZnCl2 using carbon electrodes, the
reaction that occurs at the anode is
A. Zn →
Zn2+ + 2e-
B. Zn2+ + 2e- →
Zn
C. 2Cl- →
Cl2 + 2e-
D. Cl2 + 2e- →
2Cl-
24.
In the electrolysis of aqueous zinc chloride, the half-reaction at the anode is
A. Cl2 + 2e- →
2Cl-
B. 2Cl- →
Cl2 + 2e-
C. Zn2+ +
2e- → Zn
D. Zn →
Zn2+ + 2e-
25.
The corrosion of iron can be prevented by attaching a piece of
A. Mn
B. Cu
C. Pb
D. Sn
26.
The oxidation number of carbon in CaC2O4 is
A. +2
B. +3
C. +4
D. +6
27.
To plate a nickel coin with copper,
A. the nickel coin must be the cathode.
B. the
cathode must be made out of copper
C. the
electrons must flow to the anode
D. the
solution must contain nickel ions
Consider
the following electrochemical cell for the next five questions.
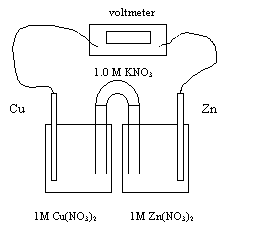
28.
Which of the following statements apply to this electrochemical cell?
I Electrons
flow through the wire toward the copper electrode.
II The
copper electrode increases in mass.
III Anions
move toward the Zn half-cell.
A. I and
II only
B. I
and III only
C. II
and III only
D. I,
II, and III
29.
The balanced equation for the overall reaction is
A. Zn
+ Cu2+ →
Cu + Zn2+
B. Cu + Zn2+ →
Zn + Cu2+
C. Zn2+ +
Cu → Cu2+ + Zn
D. Cu2+ +
Zn → Zn2+ + Cu
30.
At equilibrium the voltage of the above cell is
A. -1.10
V
B. 0.00 V
C. +0.42
V
D. +1.10
V
31.
This redox reaction occurs because
A. Zn
is a stronger oxidizing agent than Cu
B. Zn is a stronger reducing agent than Cu
C. Zn2+
is a stronger oxidizing agent than Cu2+
D. Zn2+
is a weaker reducing agent than Cu2+
32.
The initial cell voltage at 25 oC is
A. -1.10
V
B. +1.10 V
C. +0.91
V
D. +0.86
V
33.
Consider the following redox reaction:
Co2+(aq) +
2Ag(s) →
2Ag+(aq) + Co(s)
The
reaction is
A. spontaneous
and Eo is positive
B. spontaneous
and Eo is negative
C. non-spontaneous
and Eo is positive
D. non-spontaneous and Eo is
negative
34.
When MnO4- reacts to form Mn2+, the manganese
in MnO4- is
A. reduced
as its oxidation number increases
B. reduced as its oxidation number
decreases
C. oxidized
as its oxidation number increases
D. oxidized
as its oxidation number decreases
35.
The electrolyte used in the alkaline battery is
A. KCl
B. NaOH
C. H2SO4
D. KOH
36.
The electrolyte used in an automobile battery is
A. KCl
B. NaOH
C. H2SO4
D. KOH
37.
The anode used in the commercial production of Aluminum is
A. C
B. Pt
C. Al
D. AL2O3
38.
The anode and cathode used in the electrorefining of impure lead to pure lead
are
Anode Cathode
A. Pure
Pb Impure Pb
B. Impure
Pb Pure Pb
C. Pb2+ Pb
D. Pb Pb2+
39.
The anode in the LeClanche or common dry cell is
A. C
B. Zn
C. Mg
D. KOH
40.
Which of the following are electrolytic cells
I Electrowinning
II Electroplating
III Charging
a car battery
IV Fuel
cell
A. I
and II only
B. I, II, and III only
C. II
and II only
D. I,
II, III, and IV
Subjective
1. Balance the following in basic solution.
MnO4- + C2O42- →
MnO2 + CO2 (basic)
2(MnO4- + 4H+
+ 3e- →
MnO2 + 2H2O )
3(C2O42- →
2CO2 + 2e-)
Acid: 2MnO4- +
3C2O42- + 8H+ →
2MnO2 + 6CO2 + 4H2O
Basic: 2MnO4- +
3C2O42- + 4H2O →
2MnO2 + 6CO2 + 8OH-
2. Consider the electrolysis of 1.0 M H2SO4
using platinum electrodes.
a) Write
the oxidation half-reaction
H2O →
1/2O2 + 2H+ + 2e- Eo =
-0.82 V
b) Write
the reduction half-reaction
2H+ + 2e- → H2 Eo =
0.00 V
c) Write the overall reaction and determine the minimum
theoretical voltage required.
H2O → 1/2O2 + H2 Eo = -0.82 V
MTV = +0.82
V
3.
Consider the following diagram for the electrorefinning of lead.
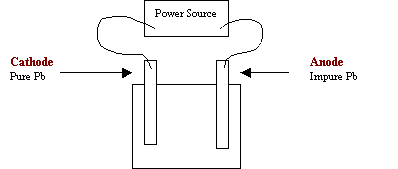
a) On the diagram, label the anode and
cathode.
b) Write the formula for a suitable electrolyte
Pb(NO3)2
c) Write the equation for the reduction
half-reaction.
Pb2+ +
2e- → Pb(s)
4. Describe two chemically
different methods that can be used to prevent corrosion of iron and explain why each method works.
Method 1: Painting
Explanation: Prevents reactants H2O
and O2 from contacting the iron
Method 2: Attach some Zn
Explanation: Fe is forced to be the cathode
and cannot oxidize
5. The data below were obtained in a redox titration of a 25.00
mL sample containing Sn2+ ions using 0.125 M KMnO4
according to the following reaction:
2MnO4- +
16H+ + 5Sn2+ → 2Mn2+ + 8H2O +
5Sn4+
Volume of KMnO4
used (mL)
Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3
Initial burette reading 2.00 13.80 24.55
Final burette reading 13.80 24.55 35.32
11.80 10.75 10.77 Average last
two to get 10.76 mL
Calculate the [Sn2+]
[Sn2+] = 0.01076
L x 0.125
mole x 5 moles Sn2+
1 L 2 moles MnO4-
0.0250
L
= 0.135 M
6. A student wanted to electroplate a coin
with copper.
a) Identify a suitable anode Cu
b) Identify an appropriate electrolyte CuSO4
c) To which battery terminal (positive or negative)
should the coin be connected?
Negative
7. Consider the electrolysis of molten
magnesium chloride.
a) Identify the product at the anode.
Cu2+
b) Write the equation for the reduction
half-reaction.
Mg2+ + 2e- ® Mg(s)
c) Write the equation for the overall
reaction.
Mg2+ + Cu ® Mg(s) + Cu2+
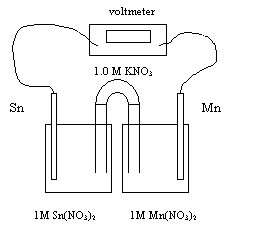 8. Consider the following electrochemical cell.
8. Consider the following electrochemical cell.
Cathode Anode
a) Write the anode reaction
Mn ® Mn2+ + 2e-
b) Write the cathode reaction
Sn2+ + 2e- ® Sn
c) Write the overall reaction and determine
the initial cell potential (Eo).
Sn2+ + Mn ® Mn2+ + Sn
d) Explain in words how the electrons move
through the cell.
From
anode Mn to cathode Sn
e) List all of the ions that migrate toward
the Sn electrode.
Sn2+ Mn2+ K+
f) Which electrode loses mass?
Anode Sn
g) What is the purpose of the salt bridge?
To allow
cations and anions to flow from one half cell to the other
h) What is the cell potential once
equilibrium is achieved?
0.00 v