Redox Quiz #4 Electrochemical
Cells/Electrolytic Cells Answers
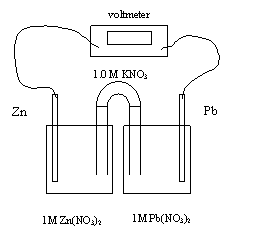
1. In the electrochemical call above, the electrons flow from
A. zinc to lead and the mass of zinc increases
B. zinc to
lead and the mass of lead increases
C. lead to zinc and the mass of zinc increases
D. lead to zinc and the mass of lead increases
2. The initial cell voltage is
A. -0.89 V
B. -0.63 V
C. +0.63 V
D. +0.89 V
3. In an operating lead-zinc electrochemical cell shown above, the cathode
A. gains mass as anions are reduced
B. loses mass as anions are reduced
C. gains mass
as cations are reduced
D. loses mass as cations are reduced
4. The equation for the half-reaction at the anode is
A. Zn2+ + 2e- → Zn
B. Pb2+ + 2e- → Pb
C. Zn →
Zn2+ + 2e-
D. Pb → Pb2+ + 2e-
5. The equation for the half-reaction at the cathode is
A. Zn2+ + 2e- → Zn
B. Pb2+
+ 2e- → Pb
C. Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
D. Pb → Pb2+ + 2e-
6. The direction of electron flow in an electrochemical cell is from
A. anode to
cathode through the external wire
B. cathode to anode through the external wire
C. anode to cathode through the external wire and back through the salt bridge
D. cathode to anode through the external wire and back through the salt bridge
7. Which of the following is formed at the anode during the electrolysis of 1.0 M NaI?
A. I2
B. O2
C. H2
D. Na
Molten MgCl2
8. As this cell operates
A. Cl- is oxidized at the anode
B. Mg2+ is oxidized at the anode
C. Cl- is oxidized at the cathode
D. Mg2+ is oxidized at the cathode
9. In an operating electrochemical cell, the anions migrate
A. towards the anode through the wire
B. towards the cathode through the wire
C. towards the
anode through the salt bridge
D. towards the cathode through the salt bridge

10. As the above electrochemical cell operates
A. nitrate ions migrate into the copper half-cell
B. copper (II) ions migrate through the salt bridge
C. magnesium
ions migrate through the salt bridge
D. potassium ions migrate into the magnesium half-cell
11. In the above electrochemical cell, the reaction at the anode is
A. Cu → Cu2+ + 2e-
B. Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
C. Mg →
Mg2+ + 2e-
D. Mg2+ + 2e- → Mg
12. In the above electrochemical cell, the initial voltage is
A. 2.03 V
B. 2.52 V
C. 2.71 V
D. 2.89 V
13. Which of the following aqueous solutions produces H2(g) and O2(g) during electrolysis
A. 1.0 M KI
B. 1.0 M CuI2
C. 1.0 M K2SO4
D. 1.0 M CuSO4
14. In the electrolysis of molten zinc chloride, the half-reaction at the anode is
A. Cl2 + 2e- → 2Cl-
B. 2Cl-
→ Cl2 + 2e-
C. Zn2+ 2e- → Zn
D. Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-

15. The initial cell voltage at 25oC is
A. -1.06 V
B. -0.54 V
C. +0.54 V
D. +1.06 V
16. The balanced equation for the overall reaction is
A. Ni+(aq) + Ag(s) → Ag+(aq) + Ni(s)
B. Ni(s) + Ag+(aq) → Ag(s) + Ni+(aq)
C. Ni2+(aq) + 2Ag(s) → 2Ag+(aq) + Ni(s)
D. Ni(s)
+ 2Ag+(aq)
→ 2Ag(s) + Ni2+(aq)
17. This redox reaction occurs because
A. Ag(s) is a stronger oxidizing agent than Ni(s)
B. Ag(s)
is a weaker reducing agent than Ni(s)
C. Ag+(aq) is a stronger reducing agent than Ni2+(aq)
D. Ag+(aq) is a weaker oxidizing agent than Ni2+(aq)

18. The direction of the electron flow is
A. from Au to Pb through the wire
B. from Pb to Au from the wire
C. from Au to Pb through the salt bridge
D. from Pb to Au through the salt bridge
19. As the cell operates
A. NO3- and K+ will migrate toward the Pb half-cell
B. NO3- and K+ will migrate toward the Au half-cell
C. NO3-
will migrate toward the Pb half-cell and K+
will migrate toward the Au half-cell
D. NO3- will migrate toward the Au half-cell and K+ will migrate toward the Pb half-cell
20. The initial voltage is
A. -1.37 V
B. 0.00 V
C. 1.37 V
D. 1.63 V
21. Which of the following is a balanced half-reaction in base?
A. Cl2 + 3H2O → ClO3- + 6H+ + 5e-
B. Cl2 + 6OH- → ClO3- + 5e- + 3H2O
C. Cl2 + 6H2O → 2ClO3- + 12H+ + 10e-
D. Cl2
+ 12OH- → 2ClO3- + 6H2O + 10e-
22. In which of the following unbalanced equations does chromium undergo oxidation?
A. Cr3+ → Cr
B. Cr3+ → Cr2+
C. Cr3+
→ Cr2O72-
D. CrO42- → Cr2O72-
23. Which of the following is formed at the anode and cathode during the electrolysis of
1.0 M Na2SO4?
Anode Cathode
A. O2 H2
B. H2 O2
C. H2 Na
D. S Na
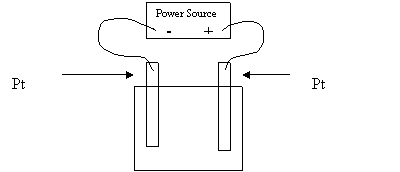
24. Consider the electrolytic cell shown in the following diagram:
Which of the following describes the anion movement and electrode masses for the above
cell?
Anion Movement Mass of Pt Electrode Mass of Cu Electrode
A. to the Cu increases increases
B. to the Cu increases decreases
C. to the Pt decreases increases
D. to the Pt decreases decreases
25. Which of the following describes electrolysis?
A. a process that uses electrical energy to cause a spontaneous reaction
B. a process that generates electrical energy using a spontaneous reaction
C. a process that uses electrical energy to
cause a non-spontaneous reaction
D. a process that generates electrical energy using a non-spontaneous reaction
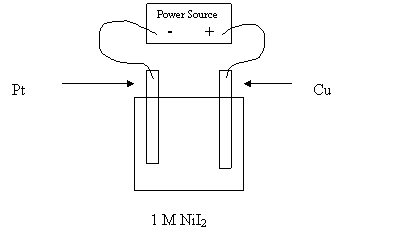
26. What products would form at the anode and cathode as this cell operates?
Anode Cathode
A.
I2
Ni
B. Ni I2
C. O2 H2
D. Cu2+ Ni
27. In the above cell, if 1.0 M NiI2 is replaced with molten NiI2, what products would form at the electrodes?
Anode Cathode
A. I2 Ni
B. Ni I2
C. O2 H2
D. Cu2+ Ni

28. In the above cell, which describes the movement of the electrons?
A. They move from left to right towards the anode.
B. They move from right to left towards the anode.
C. They move from right to left towards the cathode.
D.
They move from left to right towards the cathode.
29. Which of the following best describes what happens to the mass of the anode and the
mass of the cathode as the cell operates?
Anode Mass Cathode Mass
A. decreases increases
B. decreases no change
C. no change decreases
D. no change no change
30. What is the standard voltage E0 for the cell?
A. 0.43 V
B. 0.77 V
C. 1.34 V
D. 1.68 V