Redox Quiz #6 Corrosion
& Cathodic Protection Titration Answers
1. Which of the following metals could be used to cathodically protect a sample of lead?
A. iron
B. gold
C. silver
D. copper
2. A piece of iron can be prevented from corroding by
A. making it a cathode
B. placing it in an acidic solution
C. attaching a small piece of lead to it
D. attaching a small piece of gold to it
3. To determine the [Fe2+] in a solution of FeSO4 by e redox titration, a suitable reagent would be an acidified solution of
A. Cr3+
B. Mn2+
C. SO42-
D. Cr2O72-
4. As a metal corrodes,
A. it gains electrons
B. it becomes reduced
C. it acts as
a reducing agent
D. its oxidation number decreases
5. Which method will cathodically protect a piece of iron?
A. Paint the iron
B. Cover the iron with grease
C. Attach a piece of lead tot he iron
D. Attach a
piece of magnesium to the iron
6. Corrosion of iron can be prevented by attaching a piece of
A. Mn
B. Cu
C. Pb
D. Sn
7. A student attempted to determine the Eo (volts) of the following half-reaction:
Pd2+ + 2e- → Pd Pd2+ reacts with Cu(s) but not with Hg(l).
Based on the above, the Eo (volts) of a Pd half-cell is
A. less than 0.34 V
B. greater than 1.50 V
C. greater than 0.85 V but less than 1.50 V
D. greater than 0.34 V but less than 0.85 V
8.Consider the following redox equation:
Br2 + SO2 + Na2SO4 + 2H2O → 2H2SO4 + 2NaBr
Which of the following is gaining electrons?
A. Br2
B. SO2
C. H2O
D. Na2SO4
9. The reaction that occurs when pieces of lead, zinc, copper and silver are placed in a solution of Ni(NO3)2 is
A. Pb + Ni2+ → Pb2+ + Ni
B. Zn + Ni2+ → Zn2+ +
Ni
C. Cu + Ni2+ → Cu2+ + Ni
D. 2Ag + Ni2+ → 2Ag+ + Ni
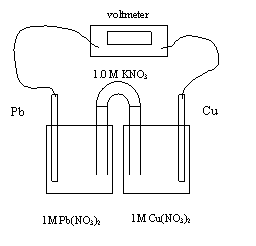
10. In the electrochemical cell above, the electrons flow from
A. copper to lead through the wire
B. lead to
copper through the wire
C. copper to lead through the salt bridge
D. lead to copper through the salt bridge
11. In the electrochemical cell above, the initial Eo value is
A. 0.03 V
B. 0.21 V
C. 0.29 V
D. 0.47 V
12. A reaction that occurs during the corrosion of iron is
A. Fe + 3e- → Fe3+
B. Fe → Fe2+ + 2e-
C. Fe2+ + 2e- → Fe
D. Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+
13. Consider the following reaction
Zn(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
What volume of 0.500 M AgNO3 is required to react completely with 6.54 g of zinc?
A. 0.0131 L
B. 0.0262 L
C. 0.200 L
D. 0.400 L
14. Consider the following diagram:
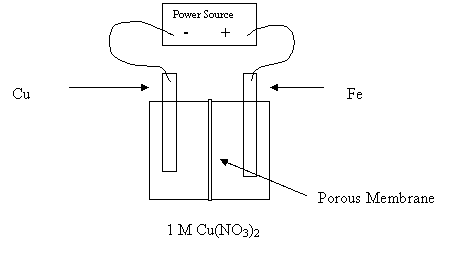
Why would this cell fail to electroplate the Fe nail with copper?
A. The Cu is inert.
B. The Fe nail is the anode.
C. The Fe nail is the cathode.
D. The porous membrane prevents reaction.
15. Consider the following diagram:
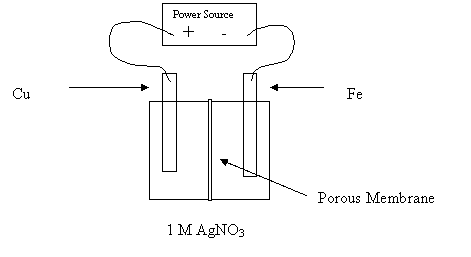
Why would this cell fail to electroplate the Fe nail with copper?
A. The Cu is the cathode.
B. The electrolyte does not contain Cu2+.
C. The Fe nail is the cathode.
D. The porous membrane prevents reaction.
16. A 10.0 mL water sample was analyzed for [Fe2+] using a redox titration with
acidified KMnO4. The equation for the reaction is:
MnO4- + 5Fe2+ + +8H+ ® Mn2+ + 5Fe3+ + 4H2O
A 10.0 mL sample was titrated with 12.5 mL of 0.100 M KMnO4 solution.
What is the [Fe2+] in the water sample?
A. 0.025 M
B. 0.13 M
C. 0.28 M
D 0.63 M
17. Why is aluminum a good choice for the manufacture of outdoor structures?
A. Pure aluminum is easily reduced.
B. Pure aluminum is not easily oxidized.
C. Pure aluminum is easily reduced, but forms a protective coating.
D. Pure aluminum is easily oxidized, but
forms a protective coating.
18. Which of the following are produced at the anode and the cathode during the
electrolysis of aqueous calcium iodide using carbon electrodes?
Anode Cathode
A. Iodine Calcium
B. Hydrogen Oxygen
C. Oxygen Hydrogen
D. Iodine Hydrogen
19. Which of the following are produced at the anode and the cathode during the
electrolysis of molten calcium iodide using carbon electrodes?
Anode Cathode
A. Iodine Calcium
B. Hydrogen Oxygen
C. Oxygen Hydrogen
D. Iodine Hydrogen
20. Which of the following are produced at the anode and the cathode during the
electrolysis of aqueous potassium fluoride using carbon electrodes?
Anode Cathode
A. Oxygen Potassium
B. Hydrogen Oxygen
C. Oxygen Hydrogen
D. Fluorine Potassium
21. Which of the following are produced at the anode and the cathode during the
electrolysis of molten potassium fluoride using carbon electrodes?
Anode Cathode
A. Oxygen Potassium
B. Hydrogen Oxygen
C. Oxygen Hydrogen
D. Fluorine Potassium
22. Two reactions involved in the refining of copper are:
Reaction I 2Cu2S + 3O2 ® 2Cu2O + 2SO2
Reaction II Cu2S + 2Cu2O ® 6Cu + SO2
What happens to the copper ions in this process?
A. They are reduced in Reaction I.
B. They are reduced in Reaction II.
C. They are oxidized in Reaction I.
D. They are oxidized in Reaction II.
23. Identify the oxidation number for manganese in MnO4-.
A. -7
B. 7
C. 8
D. 9
24. Which of the following is more difficult to reduce than the H+ ion?
A. I2
B. Ag+
C. Zn2+
D. Cu2+
25. The equation for the decomposition of nitrous acid is
3HNO2 ® 2NO + HNO3 + H2O
Which of the following is correct?
A. This is a redox reaction.
B. This is an acid-base reaction.
C. This is a reduction half equation.
D. This is an oxidation half equation.
26. An equation for the rusting of iron is shown below:
4Fe + 3O2 ® 2Fe2O3
Which of the following is false?
A. This is a redox reaction.
B. O2 is the oxidizing agent.
C. Metallic iron is reduced to Fe3+.
D. Metallic iron is the reducing agent.
27. In which of the following chemical changes will there be an oxidation number
change of +3 ?
A. Cr3+ ® Cr2+
B. ClO- ® ClO2-
C. Cr3+ ® Cr2O72-
D. Mn2+ ® MnO4-
28. Consider the following spontaneous reactions:
Cd2+ + Np ® Cd + Np3+
Cd + Pd2+ ® Pd + Cd2+
Np3+ + Ce ® Np + Ce3+
Which is the strongest oxidizing agent?
A. Cd2+
B. Ce3+
C. Np3+
D. Pd2+
29. Consider the following equation:
H3AsO4 + 4Zn + 8H+ ®AsH3 + 4Zn2+ + 4H2O
Which of the following is correct?
A. Oxygen is reduced.
B. Arsenic is reduced.
C. Zinc is the oxidizing agent.
D. The reaction is not a redox reaction.
30. What is the oxidation number of iron in magnetite, Fe3O4 ?
A. +4/3
B. +2
C. +8/3
D. +3