Chemistry 12 Test 2001
1. Consider the following experiment:
1.0 mL 0.20 M Ag+ + an unknown solution → precipitate
1.0 mL 020 M Sr2+ + an unknown solution → no precipitate
The unknown solution could contain
A 0.20 M OH- low with Ag+ and high with Sr2+
B 0.20 M NO3-
C 0.20 M PO43-
D 0.20 M SO42-
2. A compound has a solubility of 7.1 x 10-5 M at 25 oC. The compound is
A CuS
B AgBr
C CaCO3 square the solubility
D CaSO4
3. A saturated solution of NaCl contains 36.5 g of solute in 0.100 L of solution. The solubility of the compound is
A 0.062 M
B 1.60 M
C 3.65 M
D 6.24 M
4. Calculate the [Li+] in 200.0 mL of 1.5 M Li2SO4.
A 0.30 M
B 0.60 M
C 1.5 M
D 3.0 M Do not divide by L
5. The Ksp expression for a saturated solution of Mg(OH)2 is
A Ksp = [Mg2+][OH-]2
[Mg(OH)2]
B Ksp = [Mg2+][OH-]2
C Ksp = [Mg2+][OH-]
D Ksp = [Mg2+][2OH-]2
6. Consider the following saturated solution solutions
CuSO4 BaSO4 CaSO4
The order of cation concentration, from highest to lowest, is
A [Ba2+] > [Ca2+] > [Cu2+]
B [Ca2+] > [Cu2+] > [Ba2+]
C [Cu2+] > [Ca2+] > [Ba2+] largest to smallest Ksp
D [Cu2+] > [Ba2+] > [Ca2+]
7. When 1.0 x 10-3 moles of CuCl2(s) are added to 1.0 L of 1.0 x 10-3 M IO3-, the
A Trial Ksp > Ksp and a precipitate forms
B Trial Ksp < Ksp and a precipitate forms
C Trial Ksp > Ksp and no precipitate forms
D Trial Ksp < Ksp and no precipitate
forms
8. The solubility of CdS = 2.8 x 10-14 M. The value of the Ksp is
A 7.8 x 10-28 Square the solubility
B 2.8
x 10-14
C 5.6
x 10-14
D 1.7 x 10-7
9. The ion concentrations in 0.25 M Al2(SO4)3 are
[Al3+] [SO42-]
A 0.25 M 0.25 M
B 0.50 M 0.75 M
C 0.75 M 0.50 M
D 0.10 M 0.15 M
10. Which of the following will not produce a precipitate when equal volumes of 0.20 M solutions are combined?
A KOH and CaCl2
B Zn(NO3)2 and K3PO4
C Sr(OH)2
and (NH4)2S Both
have high solubility
D Na2SO4 and Pb(NO3)2
11. Consider the following equilibrium: Mg(OH)2(s) ⇄ Mg2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq)
A compound that can be added to cause a shift to the right is
A NaOH
B HCl Acids react with OH-
C Sr(OH)2
D Mg(OH)2
12. If the trial ion product for AgBrO3 is calculated to be 1.0 x 10-7, then
A a precipitate forms because the trial ion product > Ksp
B a precipitate forms because the trial ion product < Ksp
C no a precipitate forms because the trial ion product > Ksp
D no a
precipitate forms because the trial ion product < Ksp
13.Which of the following will dissolve in water to produce a molecular solution?
A CaCl2
B NaOH
C CH3OH One of these things is not kike the
other
D Sr(OH)2
14. In a solubility equilibrium, the
A rate of
dissolving equals the rate of crystallization
B neither dissolving or crystallization occurs
C concentration of solute and solvent are equal
D mass of dissolved solute is greater than the mass of the solution
15. The maximum [SO42-] that can exist in 1.0 x 10-3 M Ca(NO3)2 without a precipitate forming is
A 7.1 x 10-5 M
B 1.0 x 10-3 M
C 8.4 x 10-3 M
D 7.1 x 10-2 M
16. When equal volumes of 0.20 M CuSO4(aq) and 020 M Li2S(aq) are combined, the complete ionic equation is
A Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) → CuS(s)
B CuSO4(aq) + Li2S(aq) → CuS(s) + Li2SO4(s)
C Cu2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + 2Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) → Li2SO4(aq) + CuS(s)
D Cu2+(aq)
+ SO42-(aq) +
2Li(aq) + S2-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2Li+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
17. Consider the solubility equilibrium: CaCO3(aq) ⇄ Ca2+(aq) + CO32-(aq)
An additional piece of solid CaCO3 is added to the equilibrium above. The rate of dissolving and the rate of crystallization have
Rate of Dissolving Rate of crystallization
A increases increases
B increases not changed
C not changed increased
D not changed not changed
18. At 25 oC, which of the following compounds would dissolve to form a saturated solution with the greatest [Pb2+]?
A PbI2
B PbCl2 largest Ksp
C PbBr2
D Pb(IO3)2
19. Consider the following anions:
I 10.0 mL of 0.20 M Cl-
II 10.0 mL of 0.20 M OH-
III 10.0 mL of 0.20 M SO32-
When 10.0 mL of 0.20 M Pb(NO3)2 are added to each of the above, precipitates form in
A I and II only
B I and III only
C II and III only
D I, II, and
III
20. Which of the following units could be used to describe solubility?
A g/s
B g/L
C M/L
D mol/s
21. The solubility of SnS is 3.2 x 10-3 M. The value of the Ksp is
A 1.0 x 10-5 square the solubility
B 3.2
x 10-3
C 6.4
x 10-3
D 5.7 x 10-2
22. Silver chloride, AgCl, would be least soluble in
A 1.0 M HCl
B 1.0 M NaNO3
C 1.0 M ZnCl2
D 1.0 M AgNO3
23. The solubility of SrF2 is
A 4.3 x 10-9
B 6.6 x 10-5
C 1.0 x 10-3 square-root the Ksp
D 1.6
x 10-3
24. The Ksp expression for a saturated solution of AgCO3 is
A Ksp = [Ag2+][CO32-]
B Ksp =
[Ag+]2[CO32-]
C Ksp = [2Ag+][CO32-]
D Ksp = [2Ag+]2[CO32-]
25. How many moles of solute are dissolved in 200.0 mL of a saturated solution of FeS?
A 1.2 x 10-19
B 6.0 x 10-19
C 1.5 x 10-10
D 7.7 x 10-10
26. A solution contains both Ag+ and Mg2+ ions. During selective precipitation, these ions are removed one at a time by adding
A I-
followed by OH-
B OH- followed by S2-
C SO42- followed by
Cl-
D NO3- followed by
PO43-
27. Which of the following does not define solubility?
A the concentration of solute in a saturated solution
B the moles
of solute dissolved in a given amount of solution
C the maximum mass of solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solution
D the minimum amount of solute required to produce one litre of saturated solution
28. The ion concentrations in 0.25 M Al2(SO4)3 are
[Al3+] [SO42-]
A 0.25 M 0.25 M
B 0.50
M 0.75 M
C 0.75 M 0.50 M
D 0.10 M 0.15 M
29. Which of the following will not produce a precipitate when equal volumes of 0.20 M solutions are combined?
A KOH and SrCl2
B Zn(OH)2 and K3PO4
C Zn(OH)2 and (NH4)2S
D Na2SO4 and Pb(NO3)2
30. What is observed when H2SO4 is added to a saturated solution of CaSO4?
A CaSO4(s) dissolves
B the [Ca2+] increases
C bubbles of H2 are given off
D additional
CaSO4 precipitates
31. The solubility of CdS is 2.8 x 10-14 M. The value of the Ksp is
A 7.8 x 10-28
B 2.8
x 10-14
C 5.6
x 10-14
D 1.7 x 10-7
32. Consider the following solutions: 0.10 M Cl- 0.10 M Br- 0.10 M IO3- 0.10 M BrO3-
Equal moles of AgNO3 are added to each solution. It is observed that a precipitate forms in all but one solution. Which solution does not form a precipitate?
A Cl-
B Br-
C IO3-
D BrO3- highest Ksp
33. Consider the following equilibrium: 2O3(g) ⇄ 3O2(g) Keq = 65
Initially, 0.10 mole O3 and 0.10 mole of O2 are placed in a 1.0 L container. Which of the following describes the changes in concentrations as the reaction proceeds to equilibrium?
[O3] [O2]
A decreases decreases
B decreases increases
C increases decreases
D increases increases
34.Consider the following potential energy diagram for the reversible reaction.
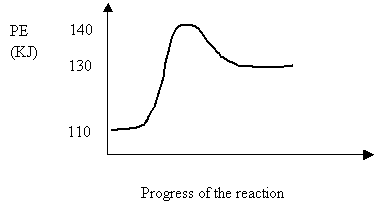
Activation Energy (kJ) ΔH (kJ)
A 10 -20
B 10 -30
C 30 +10
D 20 +30
35. Increasing the temperature of a reaction increases the rate by
I increasing frequency of collision
II increasing the kinetic energy of collision
III decreasing the potential energy of collision
A I only
B I
and II only
C II and III only
D I, II, and III
36. What is the Keq expression for the following equilibrium?
Fe (s) + 4H2O(g) ⇄ Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
A Keq = [H2]4
B Keq
= [H2]
[H2O]
C Keq
= [H2]4
[H2O]4
D Keq
= [Fe3O4][H2]4
[Fe]3[H2O]4
Subjective
1. Write the net ionic equation representing the reaction that occurs when 50.0 mL of 0.20 M ZnSO4 and 50.0 mL 0.20 M BaS are combined.
ZnSO4(aq) + BaS(aq) → BaSO4(s) + ZnS(s)
Zn2+ + SO42- + Ba2+ + S2- → BaSO4(s) + ZnS(s)
Zn2+ +
SO42-
+ Ba2+ +
S2- → BaSO4(s) + ZnS(s)
2. A 100.0 mL sample of 0.600M Ca(NO3)2 is diluted by adding 400.0 mL of water. Calculate the concentrations of all of the ions.
Ca(NO3)2 ⇄ Ca2+ + 2NO3-
(100) 0.600 M 0.120 M 0.240 M
(500)
3. When 1.00 L of CaF2 was evaporated to dryness, 2.66 x 10-2 g of residue was formed. Calculate the Ksp.
Molarity =
2.66 x 10-2 g x 1 mole
78.1 g = 3.406
x 10-4 M
1.00 L
CaF2 ⇄ Ca2+ + 2F-
3.406 x 10-4
M 3.406 x 10-4
M 6.812 x 10-4
M
Ksp =
(3.406 x 10-4 )(6.812 x 10-4)
2
= 1.58 x 10-10
4. A maximum of 0.60 g Pb(NO3)2 can be added to 1.5 L of 0.100 M NaBr(aq) without forming a precipitate. Calculate the [NaBr].
Molarity =
0.60 g x 1 mole
331.2 g = 0.001208 M
1.5 L
PbBr2 ⇄ Pb2+ + 2Br-
0.001208 M 0.100 M
Ksp = [Pb2+][Br-]2
Ksp = [0.001208][0.100]2
Ksp = 1.2 x 10 -5
5. Consider the following solutions at 25 oC
saturated AgCl(aq) saturated Ag2CO3(aq)
Using calculations, identify the solution with the greater [Ag+].
AgCl(s)
⇄ Ag+ +
Cl- Ag2CO3(s)
⇄ 2Ag+ + CO32-
x x x x 2x x
Ksp = x2 Ksp = 4x3
1.8 x 10-10 = x2 8.5 x 10-12 = 4x3
x = 1.3
x 10-5 M x = 1.286
x 10-4 M
[Ag+]
= 1.3 x 10-5 M [Ag+] =
2x = 2.6 x 10-4 M
Greater