Power Point Lesson Notes- double
click on the lesson number
Worksheets Quiz

1. Arrhenius, Bronsted
Acids, Ka and Strength. WS 1 1
2. Arrhenius, Bronsted
Bases, Kb and Strength WS 2
3. Acid & Base Reactions.
Amphiprotic. Acid Chart. WS 3 2
4. Leveling effect, Anhydrides
and Relationships. WS 4
5. Hydrolysis of Salts. WS 5 3
6. Acid, Base & Salt
Reactions. Hydrolysis. WS 6 ClassifyingEverything
Activity
7. Yamada’s Indicator Lab.
Hydrolysis. WS 7 4
8. Application of Hydrolysis and Ionization of Water Hydrolysis Quiz 1 Hydrolysis Quiz 1 Answers
Hydrolysis Quiz 2 Hydrolysis Quiz 2 Answers
9. Ionization of Water pH scale. WS 8 Hydrolysis Quiz 3 Hydrolysis Quiz 3 Answers
10. pH Calculations for
Weak Acids. WS 9
11. Ka from pH for Weak Acids. WS 10 6
12. Indicators Lab.
13. Kbs from Kas for Weak Bases. WS 11
14. pH for Weak Bases pH [H+] [
15.Amphiprotic Ions- Kas and Kbs. WS 13
16. Titration Lab. Primary Standards. Acids Midtermreview Test
17. Titration Lab
18. Buffers & Indicators WS 14 8
19. Titration Curves. WS 15 9 and 10
20. Review #1 Web Site Review Sheet Quizmebc
21. Review #2 Practice Test # 1 Practice Test 2
22. Test
WS #1 Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
1. List five properties of acids that are in
your textbook.
Acids conduct electricity, taste sour, neutralize bases, change the color of indicators, and react with some metals to produce hydrogen.
2. List five properties of bases that are in
your textbook.
Bases conduct electricity, taste bitter, neutralize acids, change
the color of indicators, and feel slippery.
3.
Make some brief notes on the commercial acids: HCl and H2SO4 (p
112).
HCl
H2SO4
4.
Make some brief notes on the commercial base NaOH - five common uses.
5.
Describe the difference between a concentrated and dilute acid (hint:
concentration refers to the molarity). Describe their relative conductivities.
Concentrated means relatively high molarity and dilute means relatively low molarity.
6.
Describe the difference between a strong and weak acid (p 121-124). Use two
examples and write equations to support your answer. Describe their relative
conductivities.
A strong acid completely ionizes and a weak acid partially ionizes.
7.
Describe a situation where a strong acid would have the same conductivity as a
weak acid (hint: think about concentration).
A weak acid could have a high molarity and the strong acid could have a low molarity.
Complete this worksheet for next period. Read pages 107-126
for homework.
Complete
each acid reaction. Label each reactant or product as an acid or base. The
first on is done for you.
1. HCN
+ H2O ⇄ H3O+ + CN-
Acid Base Acid Base
2. H3C6O7
+ H2O ⇄ H2C6O7- + H3O+
acid base base acid
3. H3PO4 + H2O ⇄ H2PO4- + H3O+
acid base base acid
4. HF
+ H2O ⇄ F- + H3O+
acid base base acid
5. H2CO3 + H2O ⇄ HCO3- + H3O+
acid base base acid
6. NH4+ + H2O ⇄ NH3 + H3O+
acid base base acid
7. CH3COOH + H2O ⇄ CH3COO- + H3O+
acid base base acid
8. HCl + H2O → Cl- + H3O+
acid base base acid
9. HNO3 + H2O → H3O+ + NO3-
acid base acid
base
Write
the equilibrium expression (Ka) for the first seven above reactions.
10.
Ka = [H3O+] [ CN-] 14. Ka = [H3O+]
[HCO3-]
![]()
![]() [HCN] [H2CO3]
[HCN] [H2CO3]
11. Ka = [H3O+]
[H2C6O7-] 15. Ka = [H3O+]
[NH3]
![]()
![]() [H3C6O7] [NH4+]
[H3C6O7] [NH4+]
12.
Ka = [H3O+] [H2PO4-] 16. Ka = [H3O+]
[CH3COO-]
![]()
![]() [H3PO4] [CH3COOH]
[H3PO4] [CH3COOH]
13.
Ka = [H3O+] [F-]
![]() [HF]
[HF]
17.
Which acids are strong? The six on the top of the
acid chart are strong.
18.
What does the term strong acid mean? They
complete ionization into ions. Such as:
HCl + H2O → Cl- + H3O+
19.
Why is it impossible to write an equilibrium expression for a strong acid? Ka = [H3O+] [Cl-]
![]() [HCl] is equal
to zero and in math numbers divided by zero are undefined. [HCl]
[HCl] is equal
to zero and in math numbers divided by zero are undefined. [HCl]
20. Which acids are weak?
All acids listed on the acid chart below the top six.
23.
What does the term weak acid mean?
Incomplete ionization. Such as: HF + H2O ⇄ F- + H3O+
24.
Explain the difference between a strong and weak acid in terms of electrical
conductivity.
A strong acid is a good conductor. A weak acid conducts but not so good.
Acid Conjugate
Base Base Conjugate Acid
14. HNO2
NO2- 15. HCOO- HCOOH
16. HSO3- SO32- 17. IO3- HIO3
18. H2O2 HO2- 19. NH3 NH4+
20. HS- S2- 21. CH3COO- CH3COOH
22. H2O OH- 23. H2O H3O+
Define:
22. Bronsted acid- a proton donor
23.
Bronsted base- a proton acceptor
24.
Arrhenius acid- a substance that ionizes in water
to produce H+
25.
Arrhenius base- a substance that ionizes in water
to produce OH-
26.
List the six strong acids. HCLO4 HI HBr
HCl HNO3 H2SO4
27.
Rank the acids in order of decreasing strength.
HCl HSO4- H3PO4 HF H2CO3
H2S
28.
What would you rather drink vinegar or hydrochloric acid? Explain.
Vinegar. It is a weak acid and produces much less H30+
ion which is the corrosive part of an acid.
Making a
Universal Indicator Lab Activity
Mix
the following indicators in a 50 mL beaker. Stir with an eyedropper.
Yamada’s
Universal Indicator
5 drops thymol blue
8 drops methyl orange
5 drops phenolphthalein
10 drops bromothymol blue
20 drops of water
Part 1. In a spot plate add two
drops of each buffer solution to a cell. Add one drop of Yamada’s indicator to
each. Record each colour on another lab sheet by colouring the cell the same
colour. Make sure you are accurate because you will use this information for
future labs and projects.
<----------
Acid Strength Increases ------ Neutral
----Base Strength Increases ------->
|
pH = 1 |
pH = 3 |
pH = 5 |
pH = 7 |
pH = 9 |
pH =11 |
pH
= 13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Part 2. Test a drop of HCl, CH3COOH,
NaOH, NH3, NaHCO3, H2CO3 and NaCl solution
for conductivity. Test with your Universal Indicator. Record the pH of each.
Test with your Universal Indicator. Explain your results with what you know
about acids and bases. Classify each as a strong or weak acid or base or
neutral, acidic, or basic salt. Write an equation for each to show how they
ionize in water using the Bronsted (Chemistry 12) definition of an acid.
Wash
and dry your acetate.
Wash
and return your eyedropper.
Wash and return your beaker.
Wash
your hands.
Results
Compound Conductivity pH Classification
HCl good 1 strong acid
CH3COOH ok 3 weak acid
NaOH good 13 strong base
NH3 ok 11 weak base
NaHCO3 good 11 weak base
H2CO3 ok 3 weak acid
NaCl good 7 neutral salt
WS # 2 Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Complete
each reaction. Label each reactant or product as an acid or base.
1. HCN + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + CN-
2. HCl + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + Cl-
3. HF + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + F-
4. F- + H2O ⇄ HF +
5. HSO4- + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + SO42-
(acid)
6. NH4+ + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + NH3
7. HPO42- + H2O ⇄ H2PO4- + OH-
(base)
Acid Conjugate Base Base Conjugate Acid
8. HCO3- CO32- 9. CH3COO- CH3COOH
10. HPO4-2
PO43- 11. IO3- HIO3
12. H2O OH- 13. NH2- NH3
14. HS- S2- 15. C2H5SO73- HC2H5SO72-
16. Circle the strong bases.
Fe(OH)3 NaOH CsOH KOH
Zn(OH)2 Sr(OH)2 Ba(OH)2 Ca(OH)2
17. Rank the following acids from strongest to weakest.
H2S CH3COOH H2PO4- HI HCl HF
5 4 6 1 1 3
18. Rank the following bases from the
strongest to weakest.
H2O F- NH3 SO32- HSO3- NaOH
6 4 2 3 5 1
19. i) Write the reaction
of H3BO3 with water (remove one H+ only
because it is a weak acid).
H3BO3 + H2O ⇄ H2BO3- + H3O+
ii) Write the Ka
expression for the above.
[H3O+]
[H2BO3-]
Ka =
[H3BO3]
iii) What is the ionization constant
for the acid (use your table). Ka = 7.3
x 10-10
20. List six strong acids. HClO4 HI HBr HCl HNO3 H2SO4
21. List six strong bases. NaOH KOH LiOH RbOH CsOH Ba(OH)2
22.
List six weak acids in order of
decreasing strength (use your acid/base table).
HIO3 H2C2O4 H2SO3 HSO4- H3PO4 HNO2
23.
List six weak bases in order of
decreasing strength (use your acid/base table).
PO43- CO32- CN- NH3 H2BO3-
HS-
WS # 3 Using Acid Strength
Tables
Acid-base reactions can be considered to be a competition
for protons. A stronger acid can cause a weaker acid to act like a base. Label
the acids and bases. Complete the reaction. State if the reactants or products
are favoured.
1. HSO4- + HPO42- ⇄ SO42- + H2PO4-
Acid Base Base Acid
Products are
favoured as HSO4- is a stronger acid than H2PO4-
2. HCN + H2O ⇄ H3O+ +
CN-
Acid Base Acid Base
Reactants are
favoured as H3O+
is a stronger acid than HCN.
3. HCO3- + H2S ⇄ H2CO3 + HS-
Base Acid Acid Base
Reactants are
favoured as H2CO3 is a stronger acid than H2S
4. HPO42- + NH4+ ⇄ H2PO4- + NH3
Base Acid Acid Base
Reactants are
favoured as H2PO4- is a stronger acid than NH4+
5. NH3 + H2O ⇄ NH4+ + OH-
Base Acid Acid Base
Reactants are
favoured as OH- is a stronger base than NH3
6. H2PO41- + NH3 ⇄ HPO42- + NH4+
Acid Base Base Acid
Products are
favoured as NH3 is a stronger base than HPO42-
7. HCO3- + HF ⇄ H2CO3 + F-
Base Acid Acid Base
Products are
favoured as HF is a stronger acid than H2CO3
8.
Complete each equation and indicate if reactants or products are favoured.
Label each acid or base.
HSO4- + HCO3- ⇄ H2CO3 + SO42-
products are
favoured
H2PO4- + HC03 ⇄ HPO42- + H2CO3 reactants are favoured
HS03- +
HPO42- ⇄ H2PO4- + SO32- products are favoured
NH3 +
HC2O4- ⇄ NH4+ + C2O42- products are favoured
9. Explain why HF(aq) is a
better conductor than HCN(aq).
HF is a stronger acid and creates more ions.
10. Which is a stronger acid in water, HCl
or HI? Explain!
Both
are strong acids and have the same strength as both completely ionize to from H+.
11. State the important ion produced by an acid and
a base.
Acid: H+ or H3O+ Base: OH-
12. Which is the stronger base? Which produces
the least OH-?
F- is the weaker base and produces the least OH- CO3-2 is the
stronger base
13. Define a Bronsted/Lowry acid and base.
An acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor.
14. Define an Arrhenius acid and base.
An acid ionizes in water to produce H+ and a base
ionizes in water to produce OH-.
15. Complete each reaction and write the
equilibrium expression.
HF + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + F- Ka= [ H3O+][ F-] Kb= [HF][ OH-]
![]()
![]() F-
+ H2O ⇄ HF +
OH- [HF] [F-]
F-
+ H2O ⇄ HF +
OH- [HF] [F-]
16. H2SO4
+ 2NaOH → Na2SO4 +
2HOH
17. Define conjugate pairs.
Acid base pairs that differ by one proton.
18.
Give conjugate acids for: HS-, NH3, HPO4-2, OH-,
H2O, NH3,
CO3-2
H2S NH4+ H2PO4- HOH H3O+ NH4+ HCO3-
19. Give conjugate bases for: NH4+,
HF, H2PO4-,
H3O+, OH-, HCO3-, H2O
NH3 F- HPO4-2 HOH O2- CO3-2 OH-
WS # 4 Acid and Basic Anhydrides
1.
What is the strongest acid that can exist in water? Write an equation to show
how a stronger acid would be reduced in strength by the leveling effect of
water.
H3O+
HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl-
2.
What is the strongest base that can exist in water? Write an equation to show
how a stronger base would be reduced in strength by the leveling effect of
water.
OH- NaOH →
Na+ + OH-
3.
List three strong acids and three strong bases.
HCl HI HClO4 NaOH KOH LiOH
4.
Rank the acids in decreasing strength:
HClO4 1 Ka is very large HClO3 2 Ka=1.2x10-2
HClO2 3 Ka=8.0x10-5 HClO 4 Ka=4.4x10-8
5. For
an oxy acid what is the relationship between the number of O’s and acid
strength? (Compare H2S04 and H2S03) The more
O’s the stronger the acid.
6.Which
acid is stronger? HI03
or HIO2
7.Which
produces more H30+? H2CO3
or HS04-
8.Which
produces more OH-? F- or HC03-
9.Which
conducts better NH3 or NaOH
(both .1M)? Why?
NaOH is a strong base.
10.Which
conducts better HF or HCN (both .1M)?
Why?
HF is a stronger acid.
11.
Compare and contrast a strong and weak acid in terms of degree of ionization,
size of ka, conductivity, and concentration of H+.
Strong acid:
complete ionization, very large Ka, good conductor, high [H+].
Weak acid:
partial ionization, small Ka, OK conductor, low [H+].
Classify each formula as an acid anhydride, basic anhydride, strong acid, weak acid, strong, or weak base. For each formula write an equation to show how it reacts with water. For anhydrides write two equations.
Formula Classification Reaction
12.
Na2O basic anhydride Na2O +
H2O →
2NaOH
13.
CaO basic
anhydride CaO +
H2O → Ca(OH)2
14.
SO3 acid anhydride SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
15.
CO2 acid anhydride CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
16.
SO2 acid anhydride SO2 + H2O → H2SO3
17.
HCl strong
acid HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl-
18.
NH3 weak base NH3 + H2O D NH4+ + OH-
19. NaOH strong base NaOH → Na+ + OH-
20.
HF weak
acid HF + H2O D H3O+ + F-
21.
H3PO4 weak acid H3PO4 + H2O D H3O+ + H2PO4-
WS # 5 Hydrolysis of Salts and
Reactions of Acids and Bases
Describe each as an acid, base, neutral salt, acidic salt, or basic salt. For each salt write a parent acid-base formation equation, dissociation equation, and hydrolysis equation (only for acidic and basic salts). For acids and bases write an equation to show how each reacts with water.
1.
NaHCO3 basic salt
H2CO3 + NaOH → NaHCO3 + H2O
NaHCO3 → Na+ + HCO3-
HCO3- + H2O ⇄ H2CO3 + OH-
2. AlCl3 acid salt
3HCl + Al(OH)3 → AlCl3 + 3H2O
AlCl3 → Al+3 + 3Cl-
Al(H2O)63+ ⇄ Al(H2O)5(OH)2+ + H+
3. NaC6H5O basic salt
C6H5OH + NaOH → NaC6H5O + H2O
NaC6H5O → Na+ + C6H5O-
C6H5O- + H2O ⇄ C6H5OH + OH-
4. Co(NO3)3 acid salt
3HNO3 + Co(OH)3 → Co(NO3)3 + 3H2O
Co(NO3)3 → Co+3 + 3NO3-
Co(H2O)63+ ⇄ Co(H2O)5(OH)2+ + H+
5. Na2CO3 basic salt
H2CO3 + 2NaOH → Na2CO3 + 2H2O
Na2CO3 → 2Na+ + CO3-2
CO3-2 + H2O ⇄ HCO3- + OH-
6.
H2C2O4 weak
acid
H2C2O4 + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + HC2O4-
7.
NH3 weak base
NH3 + H2O ⇄ NH4+ + OH-
8.
KCl neutral salt
HCl + KOH → KCl + H2O
KCl → K+ + Cl-
9.
HNO3 strong acid
HNO3 + H2O → H3O+ + NO3-
10.
RbOH strong base
RbOH → Rb+ + OH-
WS # 6 Hydrolysis of Salts and
Reactions of Acids and Bases
Describe each as an acid, base, neutral salt, acidic salt, or basic salt. For each salt write a parent acid-base formation equation, dissociation equation, and hydrolysis equation (only for acidic and basic salts). For acids and bases write an equation to show how each reacts with water.
1.
NH3 weak base
NH3 + H2O ⇄ NH4+ + OH-
2.
NaCl neutral salt
NaCl → Na+ +
Cl-
3.
HCl strong acid
HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl-
4.
NaCN basic salt
NaCN → Na+ + CN-
CN- +
H2O ⇄ HCN
+ OH-
5.
NaOH strong base
NaOH → Na+ + OH-
6.
FeCl3 acid salt
FeCl3 → Fe+3 + 3Cl-
Fe(H2O)63+ ⇄ Fe(H2O)5(OH)2+ +
H+
7.
HF weak acid
HF + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + F-
8.
LiHCO3 basic salt
LiHCO3 → Li+ + HCO3-
HCO3- + H2O ⇄ H2CO3 + OH-
9.
Fe(NO3)3 acid salt
Fe(NO3)3 → Fe+3 + 3NO3-
Fe(H2O)63+ ⇄ Fe(H2O)5(OH)2+ +
H+
10.
MgCO3 basic salt
MgCO3 → Mg+2
+ CO3-2
CO3-2 + H2O ⇄ HCO3- + OH-
11.
H2S weak acid
H2S + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + HS-
12.
HF weak acid
HF + H2O ⇄ H3O+ + F-
13.
CaI2 neutral salt
CaI2 → Ca+2 +
2I-
14.
Be(OH)2 weak base
Be(OH)2 ⇄ Mg+2 + 2OH-
15.
Ba(OH)2 strong
base
Ba(OH)2 → Ba+2 + 2OH-
16. Describe why Tums (CaCO3)
neutralizes stomach acid. It is a weak base and
will neutralize acid.
basic salt
CaCO3 → Ca+2
+ CO3-2
CO3-2 + H2O ⇄ HCO3- + OH-
17. Describe why Mg(OH)2
is used in Milk of Magnesia as an
antacid instead of NaOH.
Mg(OH)2 is strong base, however, acts like a weak base due to its low solubility, and releases OH- slowly,
whereas NaOH
is a strong base which releases OH-
Mg(OH)2(s) ⇄ Mg+2 + 2OH-
NaOH → Na+ + OH-
WS # 7 Yamada’s Indicator
Activity
Acid, Base and Salt Lab
Purpose:
1)
To use Yamada’s Indicator to determine the pH of various acids, bases and
salts.
2) To
classify compounds as strong acids, weak acids, strong bases, weak bases,
neutral salts, acid anhydrides, and basic anhydrides.
3)
To write reactions for each compound to show how each ionizes, hydrolyzes or
reacts with water.
Procedure:
1)
To a cell in a spot plate add one drop of solution or a very tiny amount of
solid. Write the formula of the compound in the data table.
2)
Add two drops of Yamada’s Indicator. Record the pH of the compound.
3)
Classify the compound as a strong acid, weak acid, strong base, weak base, neutral salt, acid anhydride, or
basic anhydride. Use the formula of the compound as well as the pH.
4)
Write an equation to show the reaction of anhydrides with water, the hydrolysis
of salts, or the ionization of acids or bases.
Data
1. Formula of compound Fe(NO3)3
pH 2
Classification acid salt
Reaction
or reactions Fe(NO3)3 → Fe+3 + 3NO3-
Fe(H2O)63+ ⇄ Fe(H2O)5(OH)2+ +
H+
2. Formula of compound NaCH3COO
pH 10
Classification basic salt
Reaction or reactions NaCH3COO → Na+ + CH3COO-
CH3COO- + H2O ⇄ CH3COOH + OH-
3. Formula of compound K2HPO4
pH 10
Classification basic salt
Reaction or reactions K2HPO4 → 2K+ + HPO4-2
HPO4-2 + H2O ⇄ H2PO4- + OH-
4. Formula of compound HCl
pH 0
Classification strong acid
Reaction or reactions HCl → H+ + Cl-
5. Formula of compound Al2(SO4)3
pH 3
Classification acid salt
Reaction or reactions Al2(SO4)3 → 2Al+3 + 3SO4-2
Al(H2O)63+ ⇄ Al(H2O)5(OH)2+ +
H+
6. Formula of compound Na2CO3
pH 12
Classification basic salt
Reaction or reactions Na2CO3 → 2Na+
+ CO3-2
CO3-2 + H2O ⇄ HCO3-
+ OH-
7. Formula of compound P2O5
pH 2
Classification acid anhydride
Reaction or reactions P2O5 + H2O → H2P2O6
H2P2O6 ⇄ H+ +
HP2O6-
8. Formula of compound Cu(NO3)2
pH 4
Classification acid salt
Reaction or reactions Cu(NO3)2 → Cu2+ + 2NO3-
Cu(H2O)62+ ⇄ Cu(H2O)5(OH)+ +
H+
9. Formula of compound Fe2(SO4)3
pH 3
Classification acid salt
Reaction or reactions Fe2(SO4)3 → 2Fe+3 + 3SO4-2
Fe(H2O)63+ ⇄ Fe(H2O)5(OH)2+ +
H+
10.
Formula of compound N2O5
pH 0
Classification acid anhydride
Reaction or reactions N2O5 + H2O → H2N2O6 → 2HNO3
HNO3 → H+ +
NO3-
11.
Formula of compound Zn(OH)2
pH 12
Classification weak base
Reaction or reactions Zn(OH)2
⇄ Zn+2 + 2OH-
12.
Formula of compound KHSO4
pH 2
Classification acid salt
Reaction or reactions KHSO4 → K+ + HSO4-
HSO4- ⇄ H+ + SO42-
13.
Formula of compound NaHCO3
pH 10
Classification basic salt
Reaction or reactions NaHCO3 → Na+ + HCO3-
HCO3- + H2O
⇄ H2CO3 + OH-
14. Formula of compound CaCO3
pH 10
Classification basic salt
Reaction or reactions CaCO3 → Ca+2 + CO3-2
CO3-2 + H2O
<⇄ HCO3-
+ OH-
15.
Formula of compound CaO
pH 12
Classification basic anhydride
Reaction or reactions CaO +
H2O →
Ca(OH)2
Ca(OH)2 → Ca+2 + 2OH-
16.
Formula of compound Al2(SO4)3
pH 3
Classification acidic salt
Reaction or reactions Al2(SO4)3 → 2Al+3 + 3SO4-2
Al(H2O)63+ ⇄ Al(H2O)5(OH)2+ +
H+
17.
Formula of compound NaCl
pH 7
Classification neutral salt
Reaction or reactions NaCl → Na+ + Cl-
WS # 8 - pH and pOH Calculations
Complete the chart:
|
|
[H+] |
[OH-] |
pH |
pOH |
Acid/base/neutral |
|
1. |
7.00 x 10-3 M |
1.43 x 10-12M |
2.155 |
11.845 |
acid |
|
2. |
1.14 x 10-13M |
8.75 x 10-2 M |
12.942 |
1.058 |
base |
|
3. |
4.7x 10-8M |
2.1 x 10-7M |
7.33 |
6.67 |
base |
|
4. |
1.0 x 10-10M |
1.0 x 10-4M |
10.00 |
4.00 |
base |
|
5. |
1.0 x 10-7M |
1.0 x 10-7M |
7.00 |
7.00 |
Neutral (2sig figs) |
|
6. |
5 x 10-4M |
2 x 10-11M |
3.3 |
10.7 |
acid |
|
7. |
2.80 x 10-3M |
3.57 x 10-12M |
2.553 |
11.447 |
acid |
|
8. |
5.0 x 10-10 M |
2.0 x 10-5M |
9.30 |
4.70 |
base |
|
9. |
2.1 x 10-5M |
4.7 x 10-10 M |
4.67 |
9.33 |
acid |
10. Calculate the [H+], [OH-]
, pH and pOH for a 0.20 M Ba(OH)2 solution.
Ba(OH)2 ⇄ Ba+2 + 2OH-
0.20M 0.20M 0.40M
[OH-]
= 0.40 M [H+] =
2.5 x 10-14 M pH =
13.60 pOH =
0.40
11. Calculate
the [H+], [OH-], pH and pOH for a 0.030 M HCl solution.
HCl → H+ + Cl-
0.030M 0.030M
[H+] = 0.030M [OH-] =
3.3 x 10-13 M pH = 1.52
pOH = 12.48
12. Calculate the [H+], [OH-],
pH and pOH for a 0.20 M NaOH solution.
NaOH
→ Na+ + OH-
0.20M 0.20M 0.20M
[OH-]
= 0.20 M [H+] =
5.0 x 10-14 M pH =
13.30 pOH =
0.70
13. 300.0 mL of 0.20 M HCl is added to 500.0 mL of water,
calculate the pH of the solution.
HCl → H+ + Cl-
300.0
x
0.20 M = 0.075 M 0.075
M pH =
-Log[H+] = 1.12
800.0
14. 200.0 mL of 0.020 M HCl is diluted to a
final volume of 500.0 mL with water, calculate the pH.
HCl → H+ + Cl-
200.0
x
0.020 M = 0.0080 M 0.0080
M pH =
-Log[H+] = 2.10
500.0
15. 150.0
mL of 0.40 M Ba(OH)2 is placed in a 500.0 mL volumetric flask and
filled to the mark with water, calculate the pH of the solution.
Ba(OH)2 → Ba2+ + 2OH-
150.0
x
0.40 M = 0.12 M 0.12 M 0.24 M
500.0
pOH =
-Log[OH-] = 0.62 pH =
14.00 - pOH
= 13.38
16. 250.0
mL of 0.20 M Sr(OH)2 is diluted by adding 350.0 mL of water,
calculate the pH of the solution.
Sr(OH)2 → Sr2+ + 2OH-
250.0
x
0.20 M = 0.083 M 0.083
M 0.1667 M
600.0
pOH =
-Log[OH-] = 0.78 pH =
14.00 - pOH
= 13.22
17. Calculate
the pH of a saturated solution of 0.40M Ba(OH)2 when 25 mL was added
25.0 mL of water.
Ba(OH)2 D Ba2+ + 2OH-
(25)0.40
M 0.20 M 0.40 M
(50)
[OH-] = 0.40
pOH
= 0.40
pH
= 13.60
WS # 9
pH Calculations for Weak Acids
1. Calculate
the [H+], [OH-], pH, and pOH for 0.20 M HCN.
HCN D H+ + CN-
I 0.20 M 0 0
C x x x
E 0.20
- x x x
x2
![]() = 4.9 x 10-10
= 4.9 x 10-10
0.20 - x
x = 9.9
x 10-6 M
[H+]
= 9.9 x 10-6 M [OH-] = 1.0 x
10-9 M pH
= 5.00 pOH = 9.00
2. Calculate
the [H+], [OH-], pH, and pOH for 2.20 M HF.
[H+]
= 2.8 x 10-2 M [OH-] = 3.6 x
10-13 M pH
= 1.56 pOH =
12.44
3. Calculate
the [H+], [OH-], pH, and pOH for 0.805 M CH3COOH.
[H+]
= 3.8 x 10-3 M [OH-] = 2.6 x
10-12 M pH
= 2.42 pOH =
11.58
4. Calculate
the [H+], [OH-], pH, and pOH for 1.65 M H3BO3.
[H+]
= 3.5
x 10-5 M [OH-]
= 2.9 x 10-10 M pH
= 4.46 pOH = 9.54
5. Calculate the pH of a saturated solution of
Mg(OH)2.
Mg(OH)2 D Mg2+ + 2OH-
x x 2x
Ksp = [Mg2+][OH-]2
5.6
x 10-12 = 4x3
[OH-] = 2x =
2.22 x 10-4 M
pH
= 10.35
6. Calculate
the pH of a 0.200 M weak diprotic acid with a Ka = 1.8 x 10-6.
H2X D H+ + HX- Note- only lose one proton
for any weak acid!!
I 0.200 M 0 0
C x x x
E 0.20
- x x x
Small
Ka approximation x = 0
x2
= 1.8
x 10-6
0.20
x = 6.0
x 10-4 M
[H+]
= 6.0 x 10-4 M [OH-] = 1.7 x
10-11 M pH
= 3.22 pOH =
10.78
7. 350.0
mL of 0.20M Sr(OH)2 is diluted by adding 450.0 mL of water,
calculate the pH of the solution.
Sr(OH)2 → Sr2+ + 2OH-
350.0
x
0.20 M = 0.0875 M 0.0875
M 0.175 M
800.0
pOH =
-Log[OH-] = 0.76 pH =
14.00 - pOH
= 13.24
WS # 10
pH Calculations for Weak Acids
1. The pH of 0.20 M HCN is 5.00. Calculate the Ka
for HCN. Compare your calculated value with that in the table.
[H+] = 10-pH = 10-5.00 =
0.0000100 M
HCN D H+ + CN-
I 0.20 M 0 0
C 0.0000100 M 0.0000100 M 0.0000100
M
E 0.19999 0.0000100 M 0.0000100
M
Ka =
(0.0000100)2 = 5.0 x 10-10
![]()
0.19999
Ka = 5.0 x 10-10
2. The pH of 2.20 M HF is 1.56. Calculate the Ka for
HF. Compare your calculated value with that in the table.
Ka = 3.5 x 10-4
3. The pH of 0.805 M CH3COOH is 2.42.
Calculate the Ka for CH3COOH. Compare your calculated value with
that in the table.
Ka = 1.8 x 10-5
4. The pH of 1.65 M H3BO3 is
4.46. Calculate the Ka for H3BO3. Compare your calculated
value with that in the table.
Ka = 7.3 x 10-10
5. The
pH of a 0.10 M diprotic acid is 3.683, calculate the Ka and identify the acid.
[H+] = 10-pH = 10-3.683 =
0.0002075 M
H2X D H+ + HX- Note a diprotic weak acid only
loses one proton.
I 0.10 M 0 0
C 0.0002075 M 0.0002075 M 0.0002075
M
E 0.09979 0.0002075 M 0.0002075
M
Ka = (0.0002075)2
= 4.3 x 10-7
0.09979
Ka
= 4.3 x 10-7 Carbonic
acid H2CO3 Look up on Ka Table.
6. The
pH of 0.20 M NH3 is 11.227; calculate the Kb of the Base.
pOH =
14.00 - pH
= 2.773
[OH-] =
10-pOH = 0.001686 M
NH3 + H2O ⇄ NH4+ + OH-
I 0.20 M 0 0
C 0.001686 M 0.001686 M 0.001686 M
E 0.1983 M 0.001686 M 0.001686 M
Kb= (0.001686)2
= 1.4 x 10-5
0.1983
7. The
pH of 0.40 M NaCN is 11.456; calculate the pH for the basic salt. Start by
writing an equation and an ICE chart.
pOH =
14.00 - pH
= 2.544
[OH-] =
10-pOH = 0.002858 M
CN- + H2O ⇄ HCN + OH-
I 0.40 M 0 0
C 0.002858
M 0.002858 M 0.002858 M
E 0.3971 M 0.002858 M 0.002858 M
Kb= (0.002858)2
= 2.1 x 10-5
0.3971
8. The pH of a 0.10 M triprotic acid is 5.068, calculate the Ka and identify the acid.
[H+] = 10-pH = 10-5.068 =
8.55 x 10-6 M
H3X D H+ + H2X- Note a triprotic weak acid only
loses one proton.
I 0.10 M 0 0
C 8.55
x 10-6 M 8.55
x 10-6 M 8.55
x 10-6 M
E 0.10 M 8.55 x 10-6 M 8.55 x 10-6 M
Ka = (8.55 x 10-6)2 =
7.3 x 10-10
0.10
Ka = 7.3 x 10-10 Boric acid H3BO3 Look up on Ka Table.
9. How many grams of CH3COOH are dissolved in 2.00
L of a solution with pH = 2.45?
[H+] = 10-2.45 = 0.003548
M
CH3COOH ⇄ H+ + CH3COO-
I x 0 0
C 0.003548 M 0.003548 M 0.003548 M
E x
- 0.003548 M 0.003548 M 0.003548 M
Keq = [H+][CH3COO-]
[CH3COOH]
1.8 x 10-5 = (0.003548)(0.003548)
[CH3COOH]
[CH3COOH] = 0.6994
M 2.00 L x 0.6994
moles x 60.0 g = 84 g
1
L 1 mole
* Use questions 1 to 4 from last assignment to mark
questions 1 to 4.
Determine
the Kb for each weak base. Write the ionization reaction for each.
Remember that Kw = Ka • Kb (the
acid and base must be conjugates). Find the base on the right side of the acid
table and use the Ka values that correspond. Be careful with
amphiprotic anions!
1.
1. NaNO2 (the basic
ion is NO2-)
2.
Kb(NO2-) = Kw = 1.0
x 10-14
Ka(HNO2) 4.6 x 10-4
3.
Kb = 2.2 x 10-11
2. 2. KCH3COO (the basic ion is CH3COO-) Kb = 5.6 x
10-10
3. 3. NaHCO3 Kb = 2.3 x 10-8
4. NH3 Kb = 1.8 x 10-5
5. NaCN Kb = 2.0 x 10-5
6. Li2HPO4 Kb = 1.6 x 10-7
7. KH2PO4 Kb = 1.3 x 10-12
8. K2CO3 Kb = 1.8 x 10-4
9.
Calculate the [H+], [OH-], pH, and pOH for 0.20 M H2CO3.
[H+] = 2.9 x 10-4 M [OH-] =
3.4 x 10-11 M pH
= 3.53 pOH =
10.47
10.
The pH of 0.20 M H2CO3 is 3.53. Calculate the Ka for H2CO3.
Compare your calculated value with that in the table.
Ka = 4.4 x 10-7
11.
Calculate the [H+], [OH-], pH, and pOH for 0.10 M CH3COOH.
[H+] = 1.3 x 10-3 M [OH-] =
7.5 x 10-12 M pH
= 2.87 pOH =
11.13
12.
The pH of 0.10 M CH3COOH is 2.87. Calculate the Ka.
[H+] = 10-2.87 = 0.001349
M
CH3COOH ⇄ H+ + CH3COO-
I 0.10 M 0 0
C 0.001349 M 0.001349 M 0.001349 M
E 0.09865 M 0.001349
M 0.001349 M
Ka = [H+][CH3COO-]
[CH3COOH]
Ka = (0.001349)( 0.001349)
(0.09865)
Ka = 1.8
x 10-5
13. 200.0 mL of 0.120 M H2SO4 reacts with 400.0 mL of 0.140 M NaOH. Calculate the pH of the resulting solution.
H2SO4 + 2NaOH ® Na2SO4 + 2HOH
0.200 L x
0.120 mol = 0.0240 mol 0.400
L x
0.140 mol = 0.0560 mol
L L

I 0.0240 mole 0.0560
mole
C 0.0240 mole 0.0480
mole
E 0 0.0080 mole
[OH-] = 0.0080
mole = 0.013 M
 0.6000
L
0.6000
L
pOH = 1.88
pH = 12.12
WS # 12 Acid and Base pH Calculations
For each weak bases
calculate the [OH-], [H+], pOH and pH. Remember that you
need to calculate Kb first.
1. 0.20 M CN-
Kb(CN-) = Kw =
1.0 x 10-14 = 2.0408 x 10-5
![]()
![]()
Ka(HCN) 4.9 x 10-10
CN- + H2O D HCN
+ OH-
I 0.20 0 0
C x x x
E 0.20
- x x x
x2 = 2.0408 x 10-5
![]()
0.20
- x
x
= [OH-] = 2.0 x 10-3 M
[OH-]
= 2.0 x 10-3 M pOH =
2.69 pH = 11.31 [H+] = 4.9 x 10-12 M
2. 0.010 M NaHS (the basic ion is HS-)
Kb = 1.1 x 10-7
[OH-] = 3.3 x 10-5
M pOH = 4.48 pH = 9.52 [H+]
= 3.0 x 10-10 M
3. 0.067 M KCH3COO
Kb = 5.55 x 10-10
[OH-] = 6.1 x 10-6
M pOH = 5.21 pH = 8.79 [H+]
= 1.6 x 10-9 M
4. 0.40 M KHCO3
Kb = 2.3 x 10-8
[OH-] = 9.6 x 10-5
M pOH = 4.02 pH = 9.98 [H+]
= 1.0 x 10-10 M
5. 0.60 M NH3
Kb = 1.786 x 10-5
[OH-] = 3.3 x 10-3
M pOH = 2.49 pH = 11.51 [H+]
= 3.1 x 10-12 M
6. If the pH of a 0.10 M weak acid HX is 3.683, calculate the Ka for
the acid and identify the acid using your acid chart.
H2X ⇄ H+ HX-
I 0.100 M 0 0
C - 0.0002075 0.0002075 0.0002075
E 0.09979 0.0002075 0.0002075
Ka = (0.0002075)2 = 4.3 x 10-7 Carbonic acid
(0.09979)
7.
Calculate the [H+], [OH-], pH, and pOH for 0.80 M H3BO3.
[H+] = 2.4 x 10-5
M [OH-]
= 4.1 x 10-10 M pH
= 4.62 pOH = 9.38
8.
Calculate the [H+], [OH-], pH, and pOH for 0.25 M H2CO3.
[H+] = 3.3 x 10-4 M [OH-] =
3.0 x 10-11 M pH
= 3.48 pOH =
10.52
9.
The pH of 1.65 M H3BO3 is 4.46. Calculate the Ka for H3BO3.
Compare your calculated value with that in the table.
Ka =
7.3 x 10-10 [OH-]
= 2.88 x 10-10 M pH =
4.46 [H+]
= 3.47 x 10-5 pOH
= 9.54
10.
The pH of 0.65 M NaX is 12.46. Calculate the Kb for NaX.
pOH
= 14.00 - 12.46
= 1.54 [OH-] = 10-1.54 =
0.02884 M
X- + H2O D HX +
OH-
I 0.65 M 0 0
C 0.02884 M 0.02884 M 0.02884 M
E 0.6212 M 0.02884 M 0.02884 M
(0.02884)2
![]() Kb =
Kb =
(0.6212)
Kb
= 1.3 x 10-3
11.
Consider the following reaction:
2HCl + Ba(OH)2 →
BaCl2 + 2H2O
When
3.16g samples of Ba(OH)2 were titrated to the equivalence point with
an HCl solution, the following data was recorded.
Trial
Volume of HCl added
#1 37.80 mL Reject
#2 35.49 mL
#3 35.51 mL Calculate
the original [HCl] = 1.04M
35.50 mL Average
2HCl + Ba(OH)2 →
BaCl2 + 2H2O
0.03550
L 3.16 g
3.16
g Ba(OH)2 x 1 mole
x 2 moles HCl
![]()
![]() Molarity =
Molarity =
171.3g 1
mole Ba(OH)2
![]()
0.03550 L
[HCl] = 1.04M
12.
Calculate the volume of 0.200M H2SO4 required to
neutralize 25.0 ml of 0.100M NaOH.
0.00625 L
13.
25.0 ml of .200M HCl is mixed with 50.0 ml .100M NaOH, calculate the pH of the
resulting solution.
No excess pH = 7.000
14.
10.0 ml of 0.200 M H2SO4 is mixed with 25.0 ml 0.200 M NaOH,
calculate the pH of the resulting solution.
pH = 12.456
15.
125.0 ml of .200M HCl is mixed with 350.0 ml .100M NaOH, calculate the pH of
the resulting solution.
pH = 12.323
16. Define standard solution and describe two ways to standardize a solution.
A standard solution is one of known molarity. If you make the solution from a weighed amount of solid and dilute it to a final volume in a volumetric flask it is a standard solution. If you titrate a solution to determine its concentration it is a standard solution.
17.
What is the [H3O+] in a solution formed by adding 60.0 mL
of water to 40.0 mL of 0.040 M KOH solution?
[H+] = 6.3 x 10-13 M
WS # 13 Review
1.
List the properties of acids/bases.
Acids- conduct electricity, taste sour, change the color of indicators,
neutralize bases, react with active metals like Mg to produce H2
gas.
Bases- conduct electricity, taste bitter, change the color of
indicators, neutralize acids, feel slippery.
2.
Define the following:
Arhenius strong acid- completely ionizes to form H+
Arhenius weak base- partially ionizes to form OH-
Bronsted strong acid- completely donates a proton to a base
Bronsted weak base- partially accepts a proton to an acid
Conjugate pair – an acid base pair that differs by one proton
Amphiprotic- a chemical species that can be an acid or base
Standard solution- a solution of known molarity
3. Show by calculation if the following
amphiprotic ions are acids or bases:
a) HCO3- Base Ka = 5.6 x 10-11 Kb
= 2.3 x 10-8
b) H2PO4- Acid Ka
= 6.2 x 10-8 Kb = 1.3 x 10-12
c) HPO42- Base Ka = 2.2 x 10-13 Kb = 1.6 x 10-7
4.
What is the strongest base in water?
What is the strongest acid in water? Write equations to explain your
answer.
Base OH- NaOH → Na+ + OH-
Acid H+ HCl →
H+ +
Cl-
5. Match each equation:
Acid/base complete HCl + NaOH →NaCl
+ HOH
Acid/base net
ionic F-
+ HOH → HF + OH-
Solubility
product H+
+ OH- → HOH
Hydrolysis AgCl(s) → Ag+ + Cl-
Acid/Base formula H20 → H+
+ OH-
Ionization of
water H+
+ Cl- + Na+ + OH-→Na++ Cl- + H2O
6. HCl and HF. Describe each acid as:
a) strong/weak
b) high/low ionization
c) large or small Ka
d) good/poor conductor
e) strong or weak electrolyte
7. 0.2M HCl and 1.0M
HF. Which is the most concentrated? Which is the strongest acid?
8. Label the scale as strong/weak acid and strong/weak base.
|________________________|_________________________|__
pH 0 7
14
SA WA WB SB
9.
Which ions are amphiprotic?
HPO4-2 HCl F- HS- H2S H2O
10.
Write the net ionic equation between any acid and base. H+ + OH- → HOH
11.
Write the ionization equation for water. H20 → H+ + OH-
12.
Write the Kw expression. Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1.0 x 10-14
13.
H2SO3 + HS- <====> H2S + HSO3-
a) Are the reactants or products favoured?
b) Are the Keq
large, small or about 1?
14.
0.20M HCl pH = 0.70
15.
0.20M Ba(OH)2 pH = 13.60
16.
0.20M H2CO3 pH = 3.53
17.
0.40M KHCO3 pH = 9.98
18.
The pH increases by 2 units. How does [H+]
change? Decreases
by a factor of 100
19.
The pH decreases by 1 unit. How does
[H+] change? Increases by a factor of 10
20.
a) For distilled water : pH = 7.00 pOH =7.00
[H+] = 1.0 x 10-7 M [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-7 M
b) For 1M HCl: pH = 0.0 pOH
=14.0 [H+] = 1 M [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-14 M
c) For 1M NaOH pH = 14.0 pOH =0.0
[H+] = 1.0 x 10-14 M [OH-] = 1 M
21.
The pH of .20M NaX is 12.50, calculate the Kb.
Kb = 5.9 x 10-3
22.
The pH of .2M HX is 4.5, calculate the Ka.
Ka = 5 x 10-9
24. 100 mL of 0.200M NaOH and 100 mL of 0.100 M KOH is mixed with 100.0 mLof 0.100M HCl.
Calculate the pH of the
resulting solution.
pH = 12.52
25.
How many grams of NaHCO3 are required to make 100mL of .200M
solution?
1.68 g
26.
What volume of 0.200M NaOH is required to neutralize 25.0 mL of 0.150M H2SO4?
0.0375 L
27.
In a titration 25.0mL of 0.200M H2SO4 is required to
neutralize 10.0mL NaOH. Calculate the concentration of the base.
1.00 M
28.
Calculate the concentration of a solution of NaCl made by dissolving 50.0g in
250 mL of water.
3.42 M
29.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇄ 2SO3(g)
4.00
moles of SO2 and 5.00 moles O2 are placed in a 2.00 L
container at 200ºC and allowed to reach equilibrium. If the equilibrium
concentration of O2 is 2.00M, calculate the Keq.
Keq = 0.500
1.
Definition (buffer) A solution that is made by mixing a weak acid or base with
a salt containing the conjugate which maintains a relatively constant pH.
2.
Acid Conjugate Base Salt
HCN
CN- NaCN
H2CO3
HCO3- KHCO3
NH4+ NH3 NH4Cl
HF F- NaF
CH3COOH
CH3COO- NaCH3COO
H2C2O4 HC2O4- Na HC2O4
3.
Write an equation for the first three buffer systems above.
HCN ⇄ H+ + CN-
H2CO3 ⇄ H+ +
HCO3-
NH3 + H2O ⇄ NH4+ + OH-
4.
Which buffer could have a pH of 4.0 ? Which buffer could have a pH of 10.0 ?
a) HCl
& NaCl b)
HF
& NaF c)
NH3 &
NH4Cl
5. Predict how the buffer of pH = 9.00 will change. Your answers are 9.00, 8.98, 9.01, 2.00, and 13.00
Final
pH
a)
2 drops of 0.10M HCl are added 8.98
b)
1 drop of 0.10M NaOH is added 9.01
c)
10 mL of 1.0 M HCl are added 2.00
6.
Write an equation for the carbonic acid, sodium hydrogencarbonate buffer
system. A few drops of HCl are added. Describe the shift and each concentration
change.
Equation: H2CO3 ⇄ H+ + HCO3-
Shift left [H+] = increases [H2CO3] = increases [HCO3-] = decreases
Indicators
1.
Definition (Indicator) A weak acid whose conjugate base is a different color.
2.
Equilibrium equation HInd ⇄ H+ +
Ind-
3.
Colors for methyl orange HInd red Ind- yellow
4.
Compare the relative sizes of [HInd] and [Ind-] at the following
pH’s.
Color Relationship
pH
= 2.0 red [Hind] > [Ind-]
pH
= 3.7 orange [Hind] = [Ind-]
pH
= 5.0 yellow [Hind] < [Ind-]
5. HCl
is added to methyl orange, describe if each increases or decreases.
[H+] increases
[HInd] increases
[Ind-] decreases
Color
Change yellow to red
6.
NaOH is added to methyl orange, describe if each increases or decreases.
[H+] decreases
[HInd] decreases
[Ind-] increases
Color
Change red to yellow
7.
State two equations that are true at the transition point of an indicator.
[Hind] = [Ind-]
Ka = [H+]
8.
What indicator has a Ka = 4 x 10-8 Neutral Red
9.
What is the Ka for methyl orange. 2 x 10-4
10. A solution is pink in phenolphthalein and colorless in thymolphthalein. What is the pH of the solution?
pH = 10
11.
A solution is blue in bromothymol blue, red in phenol red, and yellow in thymol
blue. What is the pH of the solution?
pH = 8
Choose
an indicator and describe the approximate pH of the equivalence point for each
titration. Complete each reaction.
pH Indicator
1.
HCl + NaOH -------> 7 bromothymol
blue
![]() 2. HF + RbOH -------> 9 phenolphthalein
2. HF + RbOH -------> 9 phenolphthalein
3.
HI + Ba(OH)2 -------> 7 bromothymol
blue
4.
HCN + KOH ------> 9 phenolphthalein
5.
HClO4 + NH3
-------> 5 bromocresol
green
6.
CH3COOH + LiOH
-------> 9 phenolphthalein
7.
Calculate the Ka of bromothymol blue. Ka = 2 x 10-7
8.
An indicator has a ka = 1 x 10-10, determine the indicator. Thymolphthalein
9. Calculate the Ka of methyl orange. Ka = 2 x 10-4
10.
An indicator has a ka = 6.3 x 10-13, determine the indicator. Indigo Carmine
11.
Explain the difference between an equivalence point and a transition point.
The equivalence point refers to endpoint of a titration (moles acid = moles base) and a transition point refers to when an indicator changes color.
Draw
a titration curve for each of the following.
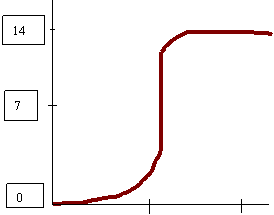
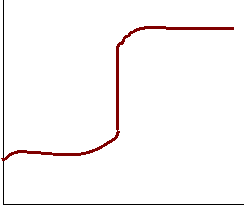
12. Adding 100 ml 1.0 M NaOH to 50 mL 1.0 M HCl 13. Adding 100 ml 1.0 M NaOH to 50 mL 1.0 M HCN
pH
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Volume of base added Volume of base added
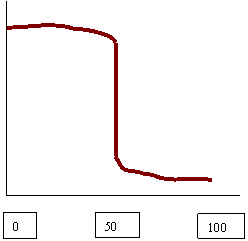
14. Adding 100 ml 0.10 M HCl to 50 mL 0.10M NH3 15. Adding 100 ml .10 M HCl to 50 mL 0.10 M NaOH
![]()

pH pH
![]()
![]()
![]()
Volume of base added Volume of base added
![]()